21 minutes
Intro to Data Analytics Fundamental with AWS Solutions
The challenges identified in many data analysis solutions can be summarized by five key challenges: volume, velocity, variety, veracity, and value.
Volume - Data Storage
- Structured(10%) data is organized and stored in the form of values that are grouped into rows and columns of a table.
- Semistructured(10%) data is often stored in a series of key-value pairs that are grouped into elements within a file.
- Unstructured(80%) data is not structured in a consistent way. Some data may have structure similar to semi-structured data but others may only contain metadata.
When businesses have more data than they are able to process and analyze, they have a volume problem.
Amazon S3
Advantages of using S3:
- Decoupling storage from processing
- Parallelization, running process in parallel
- Centralized location (reduce latency)
AWS S3 concepts
First, Amazon S3 stores data as objects within buckets.
An object is composed of a file and any metadata that describes that file. To store an object in Amazon S3, you upload the file you want to store into a bucket. When you upload a file, you can set permissions on the object and add any metadata.
Buckets are logical containers for objects. You can have one or more buckets in your account and can control access for each bucket individually. You control who can create, delete, and list objects in the bucket. You can also view access logs for the bucket and its objects and choose the geographical region where Amazon S3 will store the bucket and its contents.
Accessing your content
Once objects have been stored in an Amazon S3 bucket, they are given an object key. Use this, along with the bucket name, to access the object.
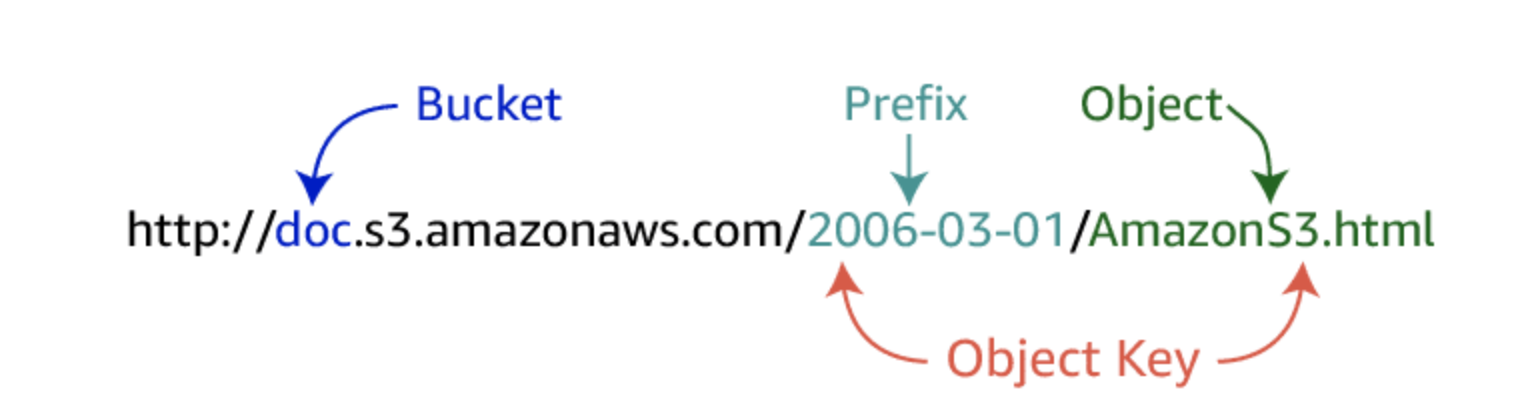
An object key is the unique identifier for an object in a bucket. Because the combination of a bucket, key, and version ID uniquely identifies each object, you can think of Amazon S3 as a basic data map between “bucket + key + version” and the object itself. Every object in Amazon S3 can be uniquely addressed through the combination of the web service endpoint, bucket name, key, and (optionally) version.
AWS Data Lakes
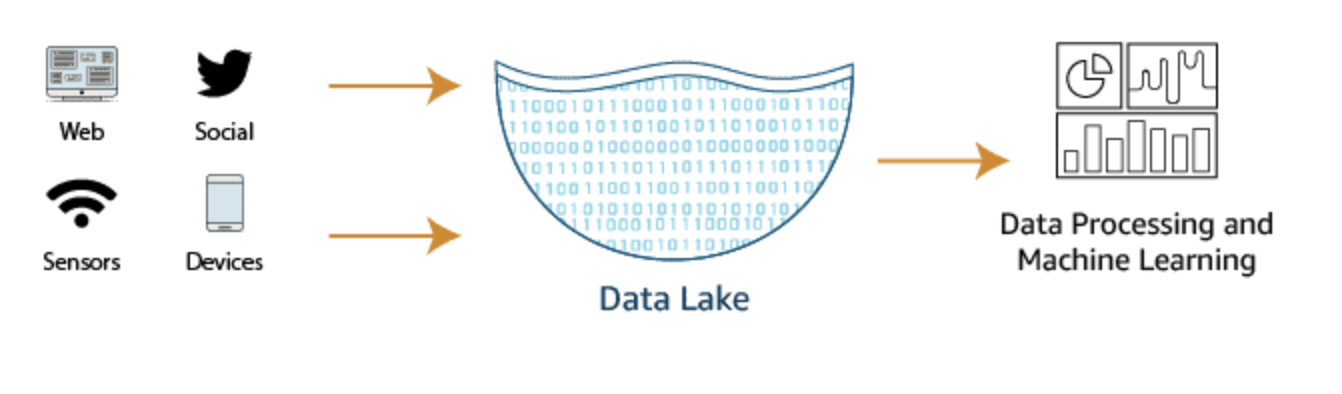
A data lake is a centralized repository that allows you to store structured, semistructured, and unstructured data at any scale.
Some cautions of data lakes:
- Single source of truth: Be careful not to let your data lake become a swamp. Enforce proper organization and structure for all data entering the lake.
- Store any type of data, regardless of structure: Be careful to ensure that data within the data lake is relevant and does not go unused. Train users on how to access the data, and set retention policies to ensure the data stays refreshed.
- Can be analyzed using AI and machine learning: Be careful to learn how to use data in new ways. Don’t limit analytics to typical data warehouse-style analytics. AI and machine learning offer significant insights.
Benefits of a data lake on AWS
- Are a cost-effective data storage solution. You can durably store a nearly unlimited amount of data using Amazon S3.
- Implement industry-leading security and compliance. AWS uses stringent data security, compliance, privacy, and protection mechanisms.
- Allow you to take advantage of many different data collection and ingestion tools to ingest data into your data lake. These services include Amazon Kinesis for streaming data and AWS Snowball appliances for large volumes of on-premises data.
- Help you to categorize and manage your data simply and efficiently. Use AWS Glue to understand the data within your data lake, prepare it, and load it reliably into data stores. Once AWS Glue catalogs your data, it is immediately searchable, can be queried, and is available for ETL processing.
- Help you turn data into meaningful insights. Harness the power of purpose-built analytic services for a wide range of use cases, such as interactive analysis, data processing using Apache Spark and Apache Hadoop, data warehousing, real-time analytics, operational analytics, dashboards, and visualizations.
AWS Lake Formation
AWS Lake Formation makes it easy to set up a secure data lake in days. A data lake is a centralized, curated, and secured repository that stores all your data, both in its original form and when prepared for analysis. A data lake enables you to break down data silos and combine different types of analytics to gain insights and guide better business decisions. AWS Lake Formation is in preview only.
AWS Lake Formation is a service that organizes and curates data within Amazon S3 data lakes. This service ensures the security and compliance of items within the lake as well as orchestrates transformation jobs utilizing the data lake and other AWS services.
Data Warehouse
structured data.
Fast, centralized data retrieval.
Data lakes and daka warehouses are two different storage systems. Data lakes are not a replacement for data warehouses.
A data warehouse is a central repository of structured data from many data sources. This data is transformed, aggregated, and prepared for business reporting and analysis.
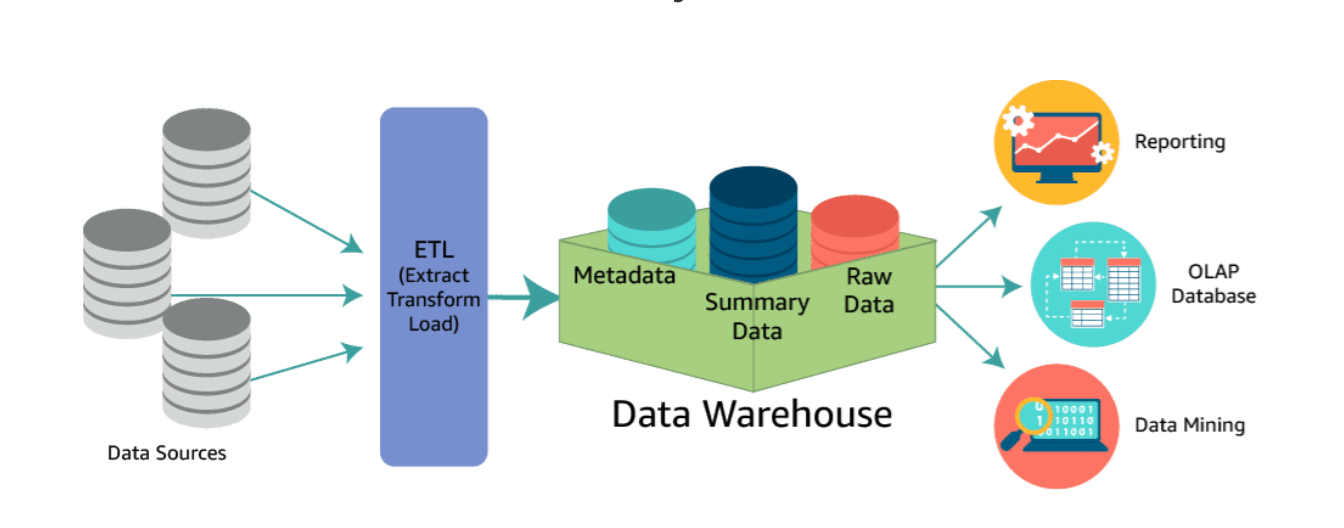
A data warehouse is a central repository of information coming from one or more data sources. Data flows into a data warehouse from transactional systems, relational databases, and other sources. These data sources can include structured, semistructured, and unstructured data. These data sources are transformed into structured data before they are stored in the data warehouse.
Data is stored within the data warehouse using a schema. A schema defines how data is stored within tables, columns, and rows. The schema enforces constraints on the data to ensure integrity of the data. The transformation process often involves the steps required to make the source data conform to the schema. Following the first successful ingestion of data into the data warehouse, the process of ingesting and transforming the data can continue at a regular cadence.
Business analysts, data scientists, and decision makers access the data through business intelligence (BI) tools, SQL clients, and other analytics applications. Businesses use reports, dashboards, and analytics tools to extract insights from their data, monitor business performance, and support decision making. These reports, dashboards, and analytics tools are powered by data warehouses, which store data efficiently to minimize I/O and deliver query results at blazing speeds to hundreds and thousands of users concurrently.
Data Marts
A subset of a data warehouse.
A subset of data from a data warehouse is called a data mart. Data marts only focus on one subject or functional area. A warehouse might contain all relevant sources for an enterprise, but a data mart might store only a single department’s sources. Because data marts are generally a copy of data already contained in a data warehouse, they are often fast and simple to implement.
Amazon Redshift Spectrum
Amazon Redshift overcomes all of data lake’s negatives by providing a cloud-based, scalable, secure environment for your data warehouse. Amazon Redshift is easy to set up, deploy, and manage and provides up to 10 times faster performance than other data warehousing solutions.
| Benefits of Amazon Redshift |
|---|
| Faster performance 10x faster than other data warehouses |
| Easy to set up, deploy, and manage |
| Secure |
| Scales quickly to meet your needs |
Data Warehouse vs Data Lakes
For analysis to be most effective, it should be performed on data that has been processed and cleansed. This often means implementing an ETL operation to collect, cleanse, and transform the data. This data is then placed in a data warehouse. It is very common for data from many different parts of the organization to be combined into a single data warehouse.
Amazon Redshift is a data warehousing solution specially designed for workloads of all sizes. Amazon Redshift Spectrum even provides the ability to query data that is housed in an Amazon S3 data lake.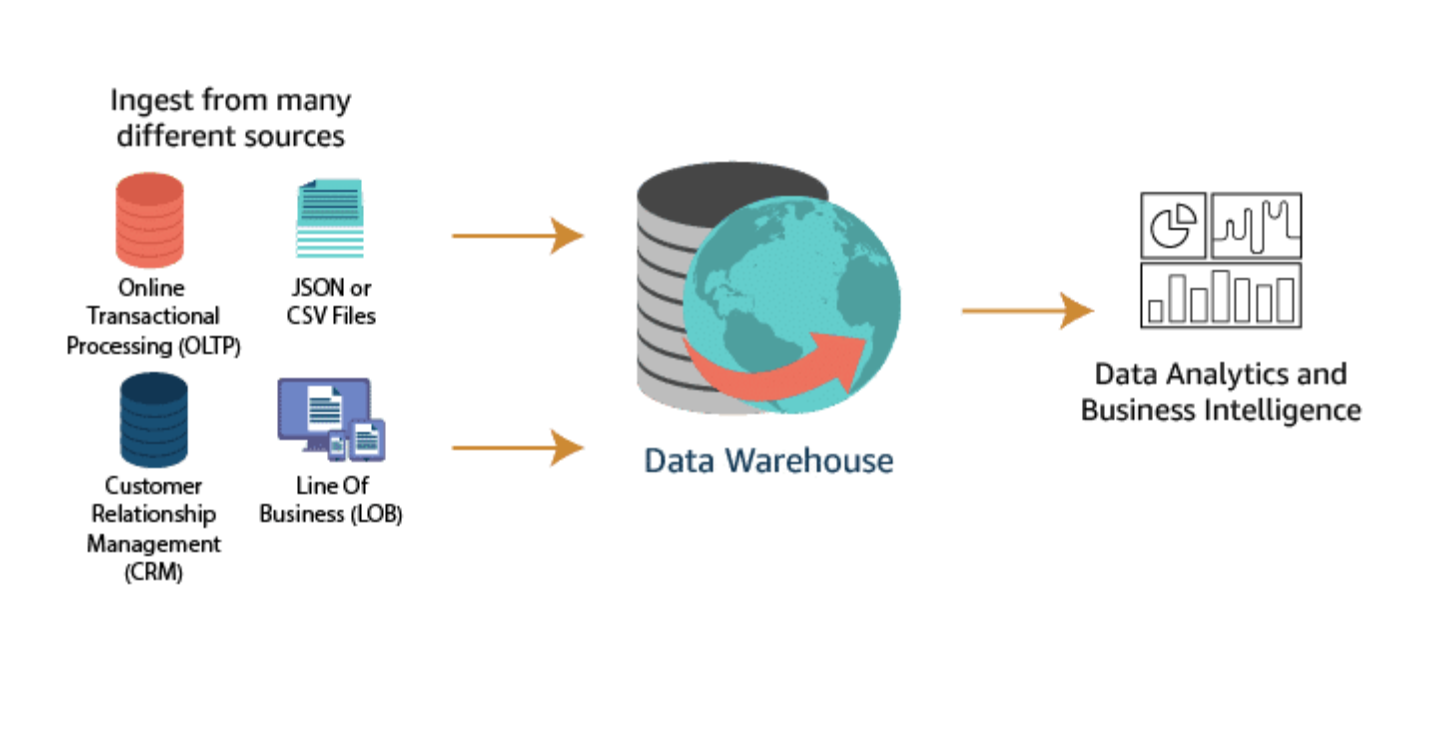
Data lakes extend data warehouses
Data lakes provide customers a means for including unstructured and semistructured data in their analytics. Analytic queries can be run over cataloged data within a data lake. This extends the reach of analytics beyond the confines of a single data warehouse.
Businesses can securely store data coming from applications and devices in its native format, with high availability, durability, at low cost, and at any scale. Businesses can easily access and analyze data in a variety of ways using the tools and frameworks of their choice in a high-performance, cost-effective way without having to move large amounts of data between storage and analytics systems.
| Characteristics | Data Warehouse | Data Lakes |
|---|---|---|
| Data | Relational from transactional systems, operational databases, and line of business applications | Non-relational and relational from IoT devices, websites, mobile apps, social media, and corporate applications |
| Schema | Designed prior to implementation (schema-on-write) | Written at the time of analysis (schema-on-read) |
| Price/ performance | Fastest query results using higher cost storage | Query results getting faster using low-cost storage |
| Data quality | Highly curated data that serves as the central version of the truth | Any data, which may or may not be curated (e.g., raw data) |
| Users | Business analysts | Data scientists, data developers, and business analysts (using curated data) |
| Analytics | Batch reporting, BI, and visualizations | Machine learning, predictive analytics, data discovery, and profiling. |
Data storage on a BIG scale
We have discussed several recommendations for storing data:
- When storing individual objects or files, we recommend Amazon S3.
- When storing massive volumes of data, both semistructured and unstructured, we recommend building a data lake on Amazon S3.
- When storing massive amounts of structured data for complex analysis, we recommend storing your data in Amazon Redshift.
Apache Hadoop
When many people think of working with a massive volume of fast-moving data, the first thing that comes to mind is Hadoop. Within AWS, Hadoop frameworks are implemented using Amazon EMR and AWS Glue. These services implement the Hadoop framework to ingest, transform, analyze, and move results to analytical data stores.
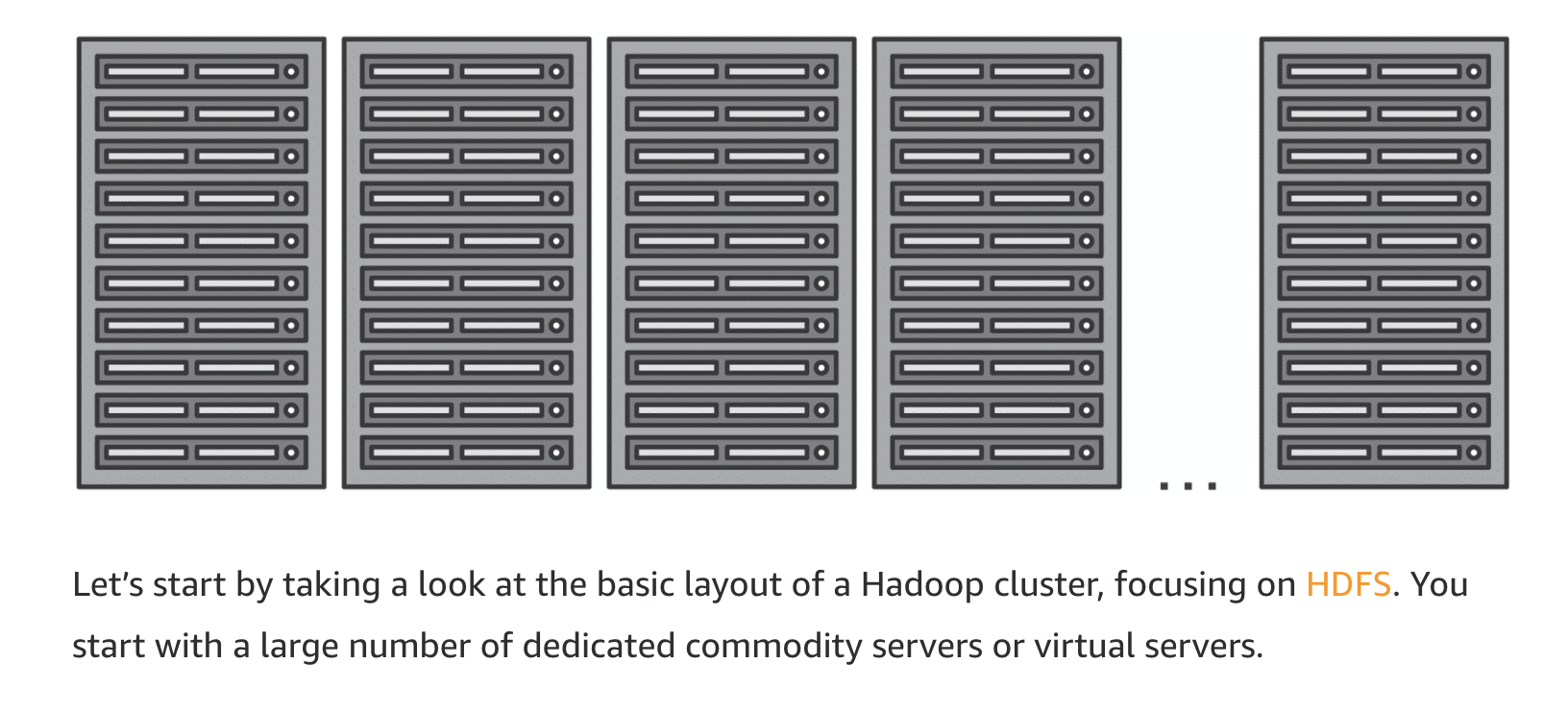
Hadoop uses a distributed processing architecture, in which a task is mapped to a cluster of commodity servers for processing. Each piece of work distributed to the cluster servers can be run or re-run on any of the servers. The cluster servers frequently use the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) to store data locally for processing. The results of the computation performed by those servers are then reduced to a single output set. One node, designated as the master node, controls the distribution of tasks and can automatically handle server failures.
Benefits of using Apache Hadoop
-
Handle uncertainty better: Hadoop facilitates data navigation, discovery, and one-time data analysis. With Hadoop, you can compensate for unexpected occurrences by analyzing large amounts of data quickly to form a response.
-
Manage Data Variety: Hadoop can process structured, semistructured, or unstructured data. This includes virtually any data format currently available.
In addition to natively handling many types of data (such as XML, CSV, text, log files, objects, SQL, JSON, and binary), you can use Haddop to transform data into formats that allow better integration into your existing data sets. Also, you can store data with or without a schema and perform large-scale ETL operations to transform your data.
-
Wide Selection of Solutions: Because Hadoop is open source, several ecosystem projects are available to help you analyze the multiple types of data Hadoop can process and analyze.
These projects give you tremendous flexibility when you are developing data analytics solutions. Hadoop’s programming frameworks (such as Hive and Pig) can support almost any data analytics use case for your applications.
-
Build for volume and velocity: Because of Hadoop’s distributed architecture, Hadoop clusters can handle tremendous amounts of data affordably. Adding additional data processing capability is as simple as adding additional servers to your cluster (horizontal scaling).
Implementing Hadoop with Amazon EMR
Amazon EMR is the AWS service that implements Hadoop frameworks. The service will ingest data from nearly any data source type at nearly any speed! Amazon EMR has the ability to implement two different file systems: HDFS or the Elastic MapReduce File System (EMRFS). A file system is a set of organizational rules that govern how files are stored.
HDFS
To handle massive volumes of data rapidly, the processing system required a way to distribute the load of reading and writing files across tens or even hundreds of high-powered servers. HDFS is distributed storage allowing files to be read and written to clusters of servers in parallel. This dramatically reduces the overall length of each and every operation.
It is helpful to understand the inner workings of an HDFS cluster. An HDFS cluster primarily consists of a NameNode, which manages the file system metadata, and DataNodes, which store the actual data.
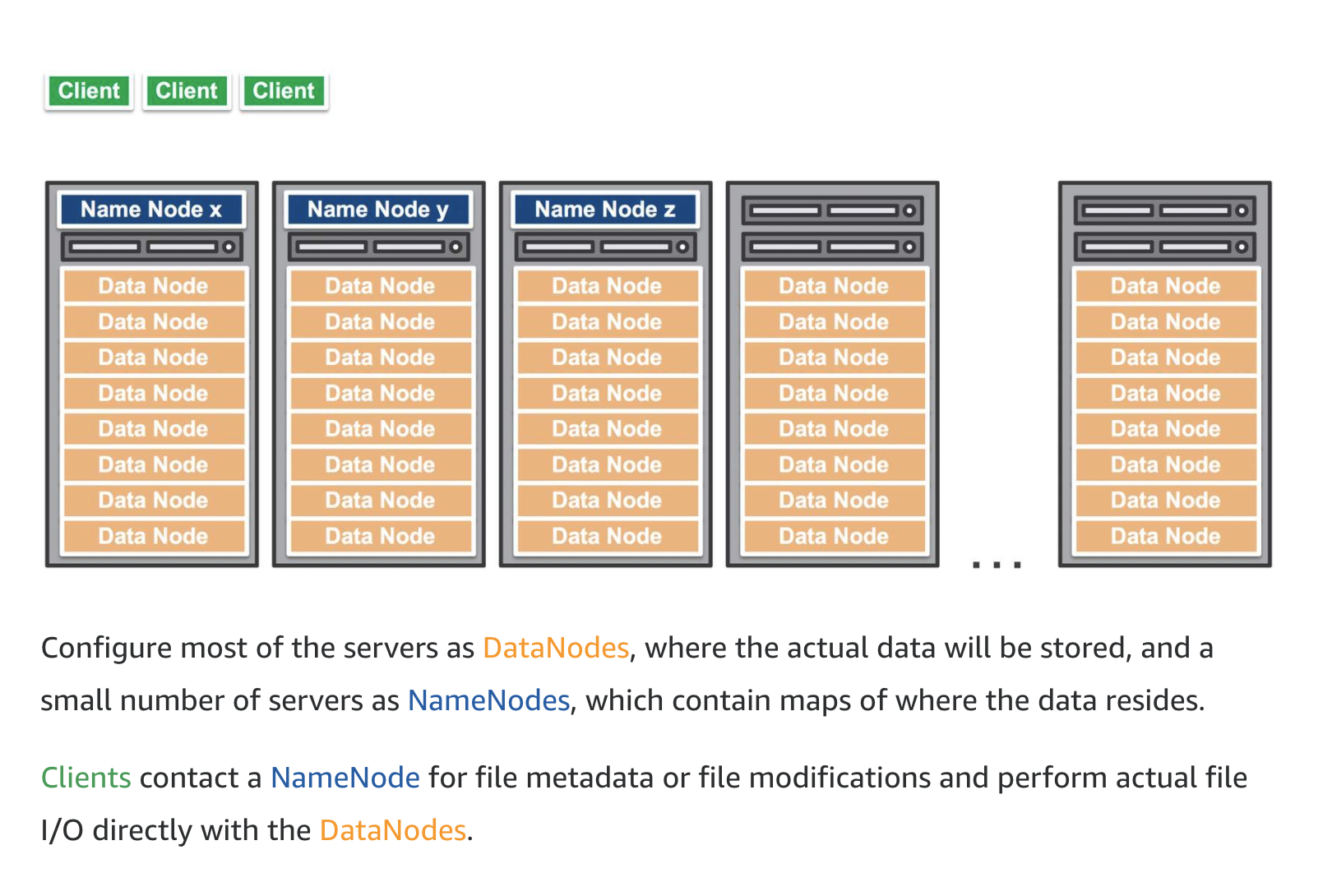
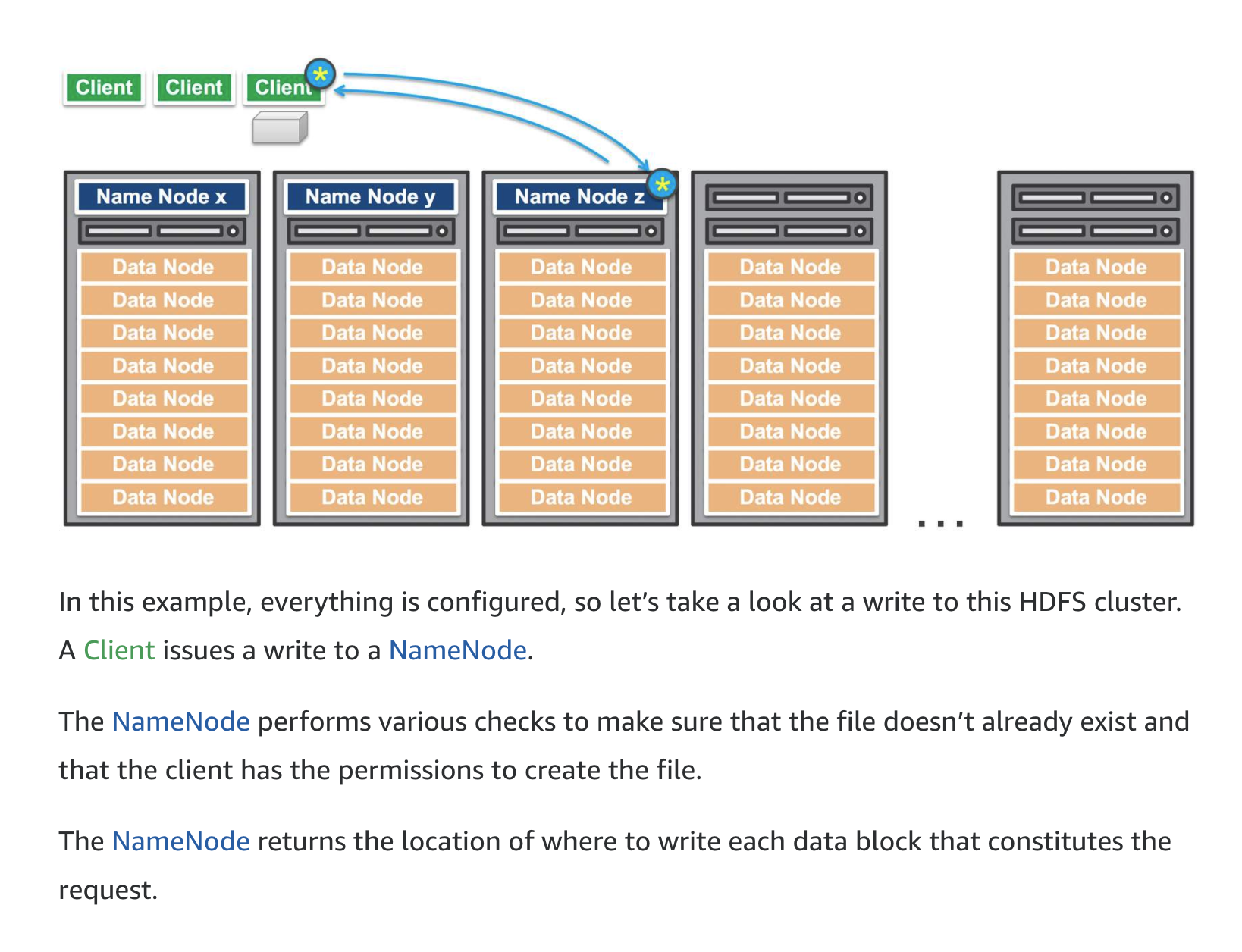
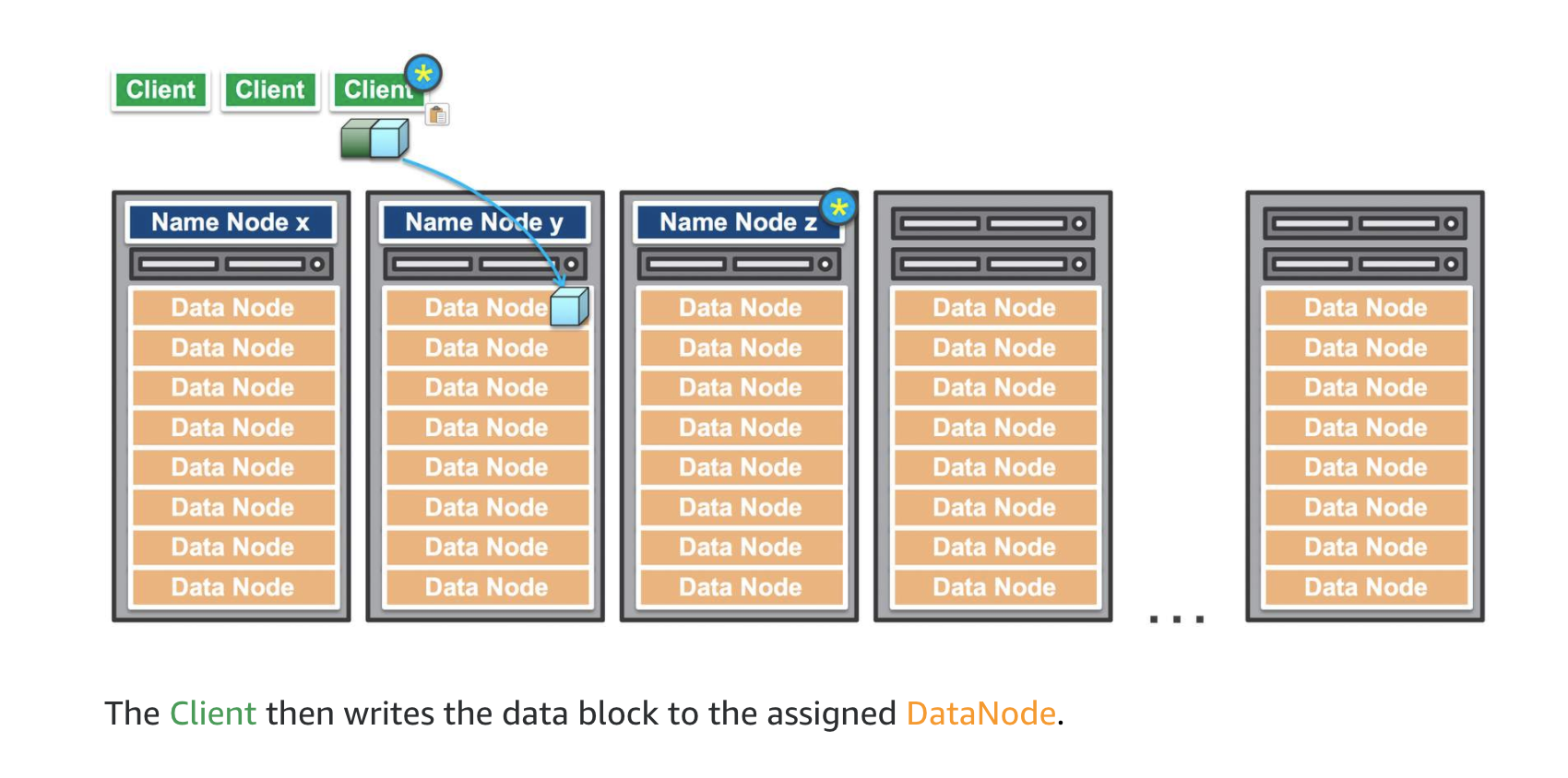

Amazon EMR is the AWS service that implements Hadoop frameworks. An Amazon EMR process begins by ingesting data from one or more data sources and storing that data within a file system. If using HDFS, the file system is stored as an elastic block store volume. This storage volume is ephemeral meaning that the storage is of a temporary nature. Once the data has been copied into the HDFS volume, the transformation and analysis of the data is performed. The results are then sent to an analytical data store, such as an Amazon S3 data lake or Amazon Redshift data warehouse.
Amazon EMRFS
Amazon EMR provides an alternative to HDFS: the EMR File System (EMRFS). EMRFS can help ensure that there is a persistent “source of truth” for HDFS data stored in Amazon S3. When implementing EMRFS, there is no need to copy data into the cluster before transforming and analyzing the data as with HDFS. EMRFS can catalog data within a data lake on Amazon S3. The time that is saved by eliminating the copy step can dramatically improve performance of the cluster.
Velocity - Data Processing
- Batch processing
- scheduled batch processing
- Periodic batch processing
- Streaming Processing
- Near-real-time
- Real-time
Characteristics of data processing velocity
Velocities on collecting data
| Data Processing | Velocities on Collecting Data |
|---|---|
| Batch: | Velocity is very predictable with batch processing. It amounts to large bursts of data transfer at scheduled intervals. |
| Periodic: | Velocity is less predictable with periodic processing. The loss of scheduled events can put a strain on systems and must be considered. |
| Near real-time: | Velocity is a huge concern with near real-time processing. These systems require data to be processed within minutes of the initial collection of the data. This can put tremendous strain on the processing and analytics systems involved. |
| Real-time: | Velocity is the paramount concern for real-time processing systems. Information cannot take minutes to process. It must be processed in seconds to be valid and maintain its usefulness. |
Velocities on processing data
| Data Processing | Velocities on Processing Data |
|---|---|
| Batch and periodic: | Once the data has been collected, processing can be done in a controlled environment. There is time to plan for the appropriate resources. |
| Near real-time and real-time: | Collection of the data leads to an immediate need for processing. Depending on the complexity of the processing (cleansing, scrubbing, curation), this can slow down the velocity of the solution significantly. Plan accordingly. |
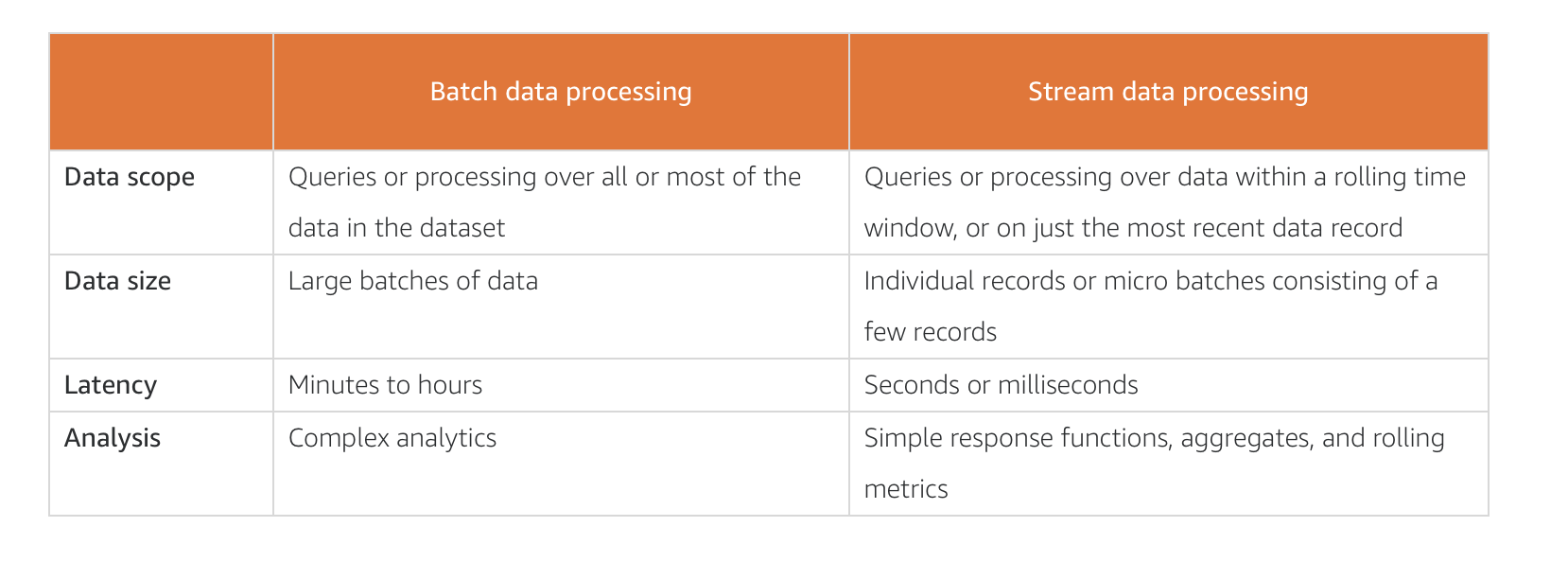
*Attributes of batch and stream processing*
The table below highlights the difference between batch and stream processing:
Business Challenge
The slower collection of data followed by a rapid processing requirement is a common challenge.
The rapid collection of data followed by the rapid processing of data is a common signature of streaming analytics.
Batch processing architecture
Batch processing can be performed in different ways using AWS services. i.e.,
S3, Lambda, EMR, Glue, Redshift.
Amazon EMR provides a managed Hadoop framework that makes it easy, fast, and cost-effective to process vast amounts of data across dynamically scalable Amazon EC2 instances.
Amazon EMR is a managed service for executing highly complex, massive batch workloads. This service also allows highly complex analytic operations.
AWS Glue is a fully managed extract, transform, and load (ETL) service that makes it easy for you to prepare and load your data for analytics.
Amazon Redshift is a fast, scalable data warehouse that makes it simple and cost-effective to analyze all your data across your data warehouse and data lake.
Amazon Redshift is a managed data warehouse service that stores large amounts of transactional data for the purpose of analytics.
AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that can be used to trigger processing operations in a batch processing system.
Stream Data Processing
AWS Knesis
Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose is the easiest way to capture, transform, and load data streams into AWS data stores for near real-time analytics with existing business intelligence tools.
Amazon Kinesis Data Analytics is the easiest way to process data streams in real time with SQL or Java without having to learn new programming languages or processing frameworks.
…
Other stream processing architecture:
Amazon Athena is an interactive query service that makes it easy to analyze data in Amazon S3 using standard SQL. Athena is serverless, so there is no infrastructure to manage, and you pay only for the queries that you run.
Amazon QuickSight is a fast, cloud-powered business intelligence (BI) service that makes it easy for you to deliver insights to everyone in your organization.
Variety – data structure and types
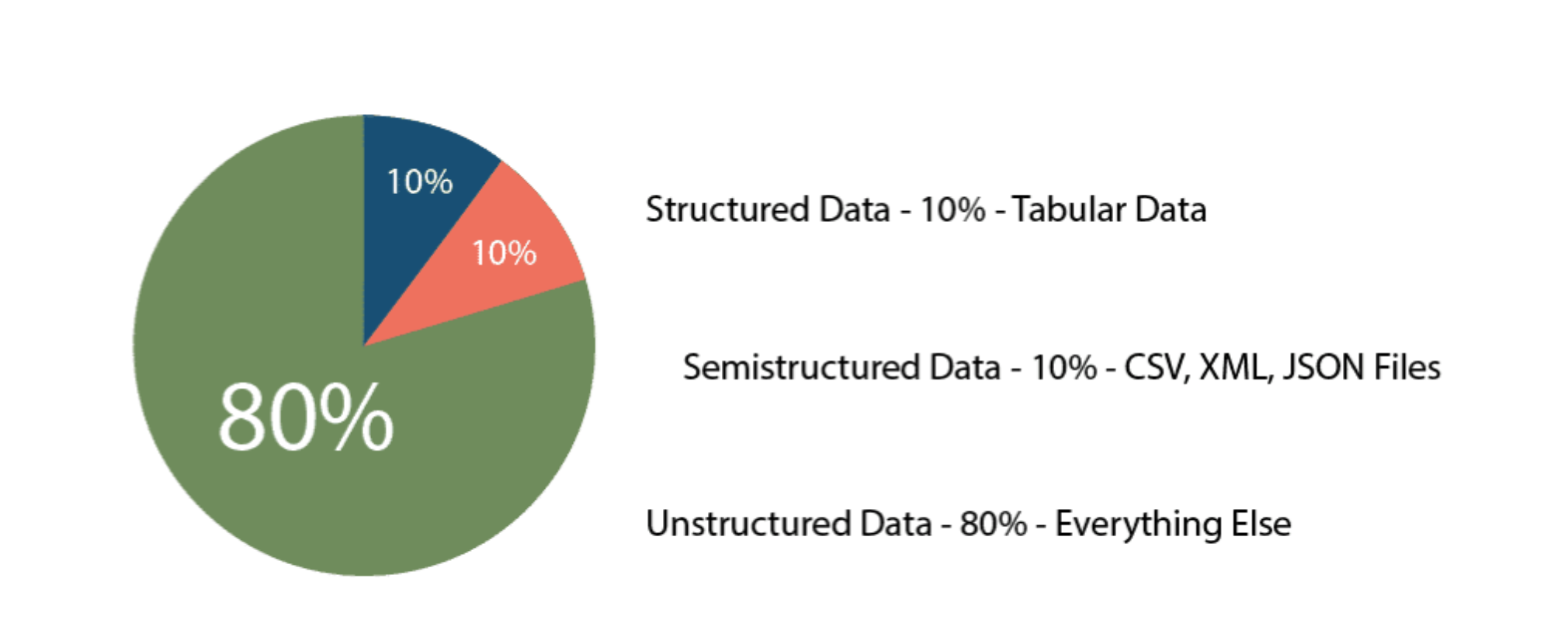
Surprisingly, the most common data types auch as csv and JSON are semistructured data.
Intro to Structured Data Stores
Flat-file Data
Flat-file data generally resides in a worksheet or spreadsheet.
Relational databases
A process known as normalization helps a business take flat-file data and turn it into a relational database. Normalization is a set of rules that work together to reduce redundancy, increase reliability, and improve the consistency of data storage.
Types of information systems
There are two main ways—known as information systems—of organizing data within a relational database. The data can be organized to focus on the storage of transactions or the process of analyzing transactions.
Transactional databases are called online transaction processing (OLTP) databases. The data gathered by OLTP databases is often fed into another type of database that focuses on analyzing the transactional data. Online analytical processing (OLAP) databases gather data from OLTP systems for the purpose of organizing it for analytical operations.
*Comparing OLTP and OLAP*
| Characteristic | OLTP | OLAP |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Constant transactions (queries/updates) | Periodic large updates, complex queries |
| Examples | Accounting database, online retail transactions | Reporting, decision support |
| Type | Operational data | Consolidated data |
| Data retention | Short-term (2-6 months) | Long-term (2-5 years) |
| Storage | Gigabytes (GB) | Terabytes (TB)/petabytes (PB) |
| Users | Many | Few |
| Protection | Robust, constant data protection and fault tolerance | Periodic protection |
In an OLTP system, the most common queries are called lookup queries. These queries need to return several columns of data for each matching record. The filters on this data are generally based on the key columns in that table. In this type of system, you might query to get details for a specific order.
In an OLAP system, the most common queries are aggregate queries. These queries take large numbers of rows and reduce them to a single row by aggregating the values in one or more columns. In this type of system, you might query to find out the total number of items sold on a specific date.
| Row-based indexes | Columnar indexes | |
|---|---|---|
| Storage on disk | Row by row | Column by column |
| Read/write | Best at random reads and writes | Best at sequential reads and writes |
| Best for | Returning full rows of data based on a key | Returning aggregations of column values |
| Implementation | Transactional systems | Analytical processing |
| Data compression | Low to medium compression can be achieved | High compression is the norm |
AWS Solution:
Within AWS, the Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) provides the needs for many different relational database management systems. It supports the most popular database engines including Amazon Aurora, MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle, and SQL Server.
**Amazon Redshift **is a fast, scalable data warehouse that makes it simple and cost effective to analyze all your data across your data warehouse and data lake. Amazon Redshift delivers 10 times faster performance than other data warehouses by using machine learning, massively parallel query execution, and columnar storage on high-performance disk. You can set up and deploy a new data warehouse in minutes and run queries across petabytes of data in your Amazon Redshift data warehouse and exabytes of data in your data lake built on Amazon S3.
Amazon Redshift implements columnar indexing to achieve the the right performance for analytical workloads.
Intro to Semistructured and Unstructured Data Stores
Semistructured and unstructured data are often stored in non-relational database systems, sometimes called NoSQL databases.
Data Schemas
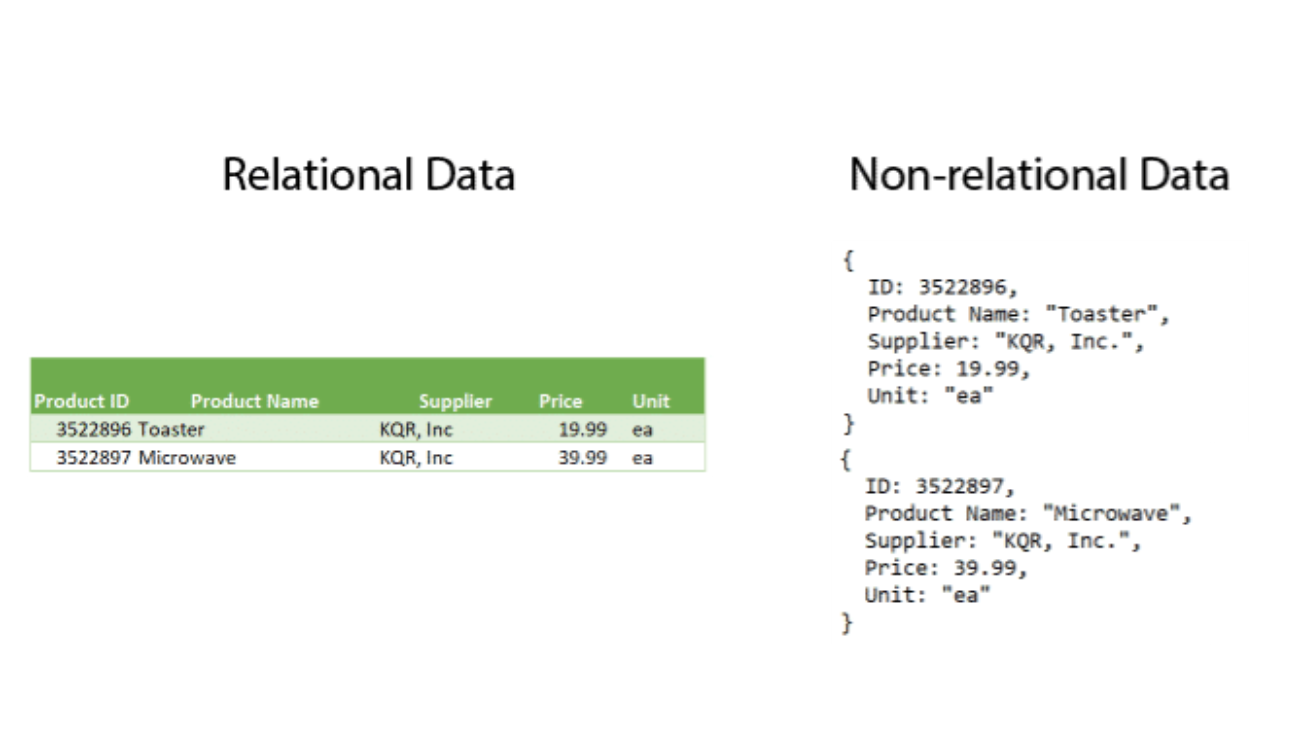
AWS Solutions:
Amazon DynamoDB is a key-value and document database that delivers single-digit millisecond performance at any scale. It’s a fully managed, multiregion, multimaster database with built-in security, backup and restore, and in-memory caching for internet-scale applications. DynamoDB can handle more than 10 trillion requests per day and support peaks of more than 20 million requests per second.
Graph databases
Graph databases are purpose-built to store any type of data: structured, semistructured, or unstructured. The purpose for organization in a graph database is to navigate relationships. Data within the database is queried using specific languages associated with the software tool you have implemented.
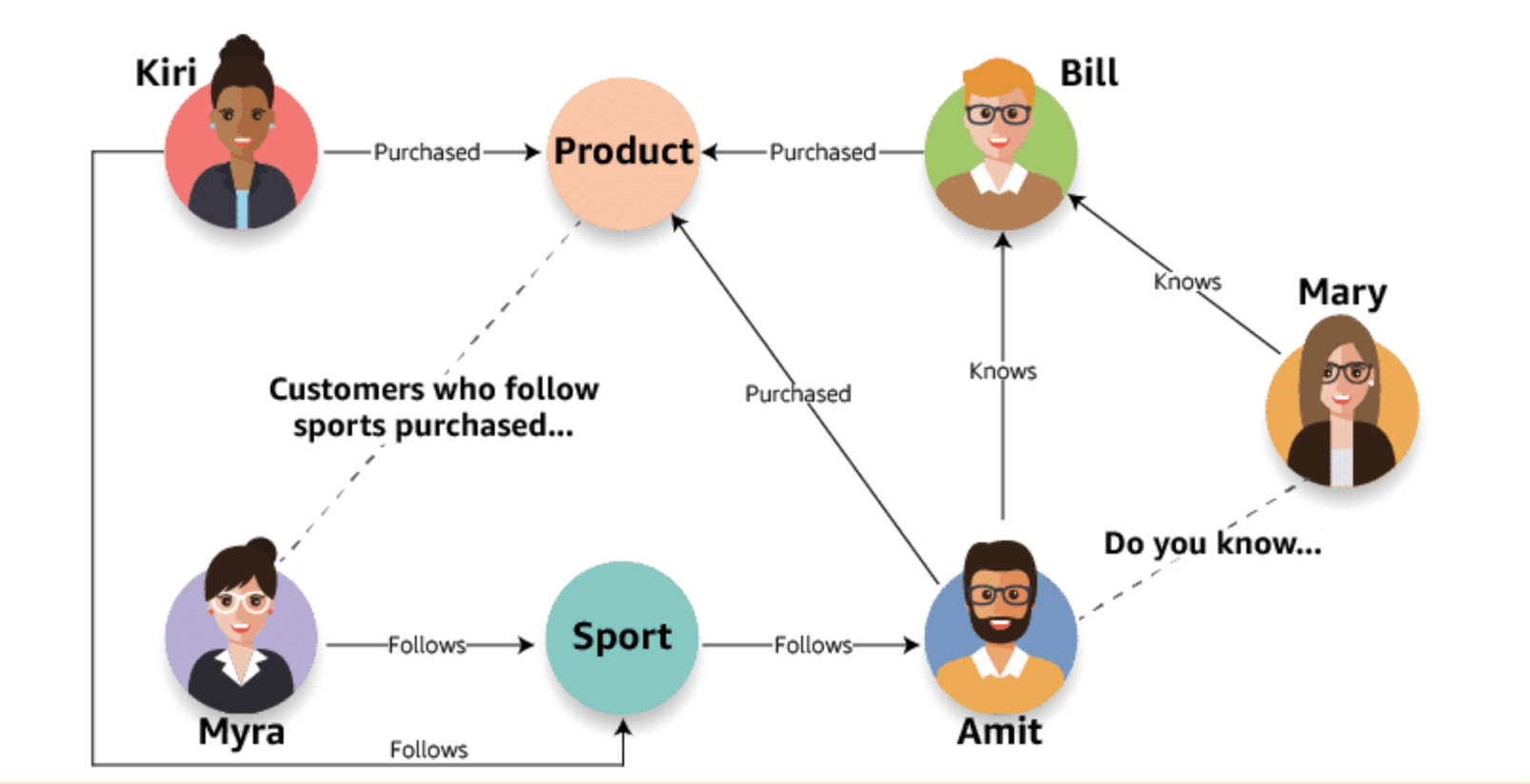
The AWS Solution:
Amazon Neptune is a fast, reliable, fully managed graph database service that makes it easy to build and run applications that work with highly connected data sets.
The core of Neptune is a purpose-built, high-performance graph database engine optimized for storing billions of relationships and querying the graph with milliseconds latency.
| Characteristic | Relational | Non-relational | Graph |
|---|---|---|---|
| Representation | Multiple tables, each containing columns and rows | Collection of documents Single table with keys and values | Collections of nodes and relationships |
| Data design | Normalized relational or dimensional data warehouse. | Denormalized document, wide column or key value | Denormalized entity relationship |
| Optimized | Optimized for storage | Optimized for compute | Optimized for relationships |
| Query style | Language: SQL | Language: many Uses object querying | Language: many Uses object querying |
| Scaling | Scale vertically | Scale horizontally | Hybrid |
| Implementation | OLTP business systems, OLAP data warehouse | OLTP web/mobile apps | OLTP web/mobile apps |
A multidemensional data warehouse is best suited for a relational database.
Log files are generally produced in the form of XML or JSON files, which are very well suited for storage in a document database.
Data collected from online gaming websites is often very rapid in generation and temporary in nature. This data is well suited for a key-value database.
Transactional data from a social subscription service could be stored in a relational database, but due to the social component, it would be better suited to the advantages gained by using a graph database.
Remark: Horizontal vs Vertical Scaling
Scalable Dimensions:
-
concurrent Connections,
-
CPU high or low
-
Memory(Quantity + Speed)
-
Netword Interfaces
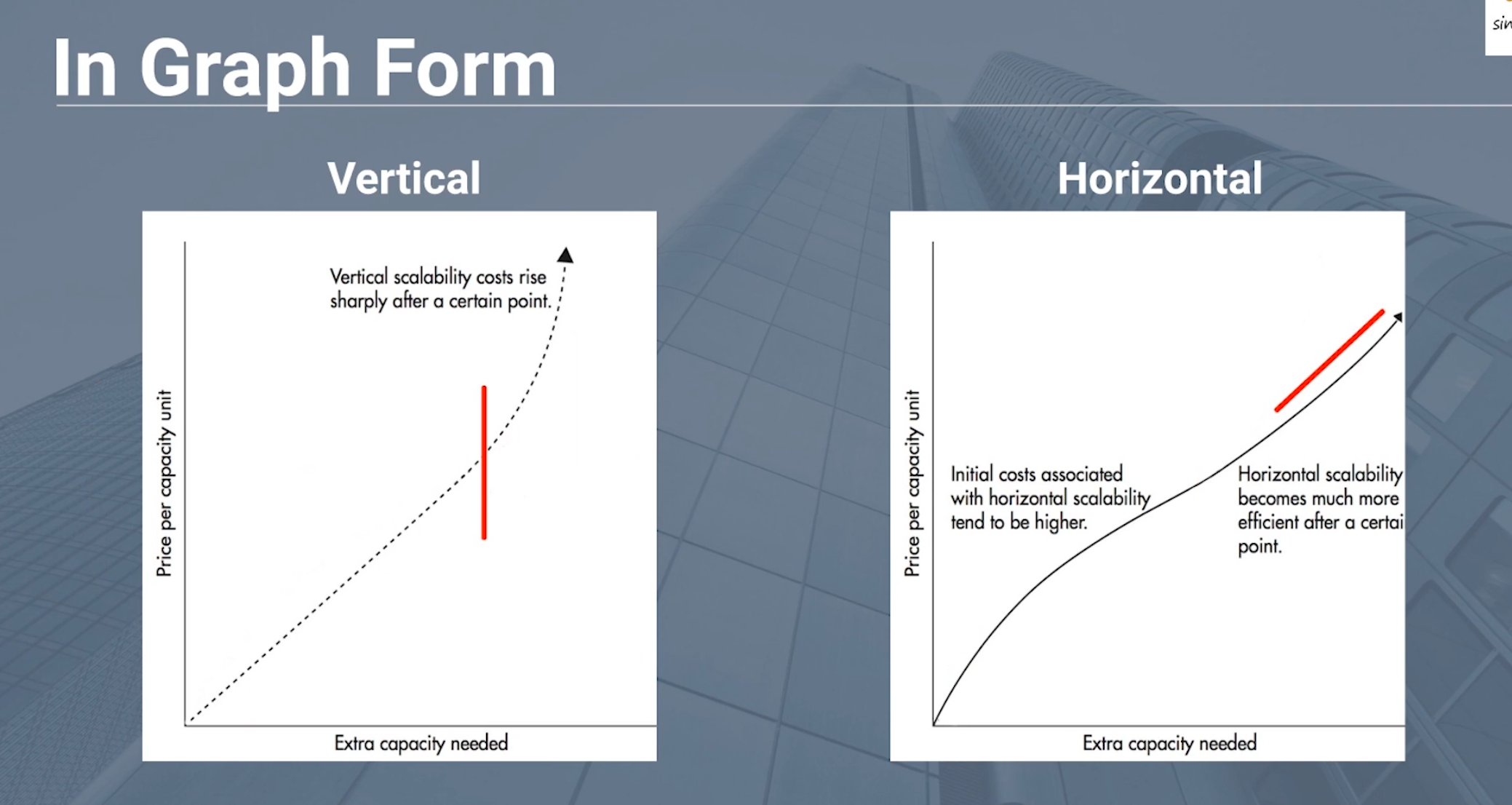
Scale Horizontally by adding more nodes and a load balancer.
Horizontal has more startup cost, but better efficiency and safer.
Scale Vertically by adding more powerful hardware.
Vertical has lower cost efficiency and a theoretical maximum.
Veracity - Cleansing and Transformation
Definitions
Curation is the action or process of selecting, organizing, and looking after the items in a collection. Data integrity is the maintenance and assurance of the accuracy and consistency of data over its entire lifecycle. Data veracity is the degree to which data is accurate, precise, and trusted.
Understanding database consistency - ACID and BASE
ACID
ACID is an acronym for Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability. It is a method for maintaining consistency and integrity in a structured database.
BASE
BASE is an acronym for Basically Available Soft state Eventually consistent. *It is a method for maintaining consistency and integrity in a structured or semistructured database.
| ACID compliance | BASE compliance |
|---|---|
| Strong consistency | Weak consistency – stale data is OK |
| Isolation is key | Availability is key |
| Focus on committed results | Best effort results |
| Conservative (pessimistic) availability | Aggressive (optimistic) availability |
AWS Solution
When it comes to performing the data transformation component of ETL, there are two options within AWS: Amazon EMR and AWS Glue. These two services provide similar results but require different amounts of knowledge and time investment.
Amazon EMR is a more hands-on approach to creating your data pipeline. This service provides a robust data collection and processing platform. Using this service requires you to have strong technical knowledge and know-how on your team. The upside of this is that you can create a more customized pipeline to fit your business needs. Additionally, your infrastructure costs may be lower than running the same workload on AWS Glue.
AWS Glue is a serverless, managed ETL tool that provides a much more streamlined experience than Amazon EMR. This makes the service great for simple ETL tasks, but you will not have as much flexibility as with Amazon EMR. You can also use AWS Glue as a metastore for your final transformed data by using the AWS Glue Data Catalog. This catalog is a drop-in replacement for a Hive metastore.
Value - Reporting and Business Intelligence
-
What were total sales in April?
Questions relating to past events are answered using descriptive analytics.
-
What is the year-over-year total sales for the Asia Pacific region?
Questions comparing current data sets to past data sets are answered using diagnostic analytics.
-
What is the projected growth for smoking-related hospitalizations next year?
Questions looking for predictions of future events are answered using predictive analytics.
-
What products should I buy if I like the Seattle Seahawks?
Questions looking for recommendations based on preferences or prior purchase history are answered using prescriptive analytics.
-
What is the average number of vehicles spotted by my video doorbell?
Questions that require analysis of video, images, and voice are answered using cognitive analytics.
AWS Solutions:
Amazon QuickSight is a fast, easy-to-use, cloud-powered business analytics service that makes it easy for all employees within an organization to build visualizations, perform one-time analyses, and quickly get business insights from their data, any time, on any device.
Interactive dashboards provide dashboard consumers with a self-service way to consume and slice and dice their data to answer questions without having to rely on a business intelligence team.