28 minutes
AWS Machine Learning Exam Readiness with Sample Questions
These are my study notes directly from AWS Training cource - AWS Machine Learning Exam Readiness.
Domain 1: Data Engineering
Create Data Repo for Machine Learning
Identify and implement a data ingestion solution
To use the data for ML, you need to ingest it into a service like Amazon S3
Batch and stream processing are two kinds of data ingestion.
Batch processing
Batch processing periodically collects and groups source data.
With batch processing, the ingestion layer periodically collects and groups source data and sends it to a destination like Amazon S3. Batch processing is typically used when there is no real need for real-time or near-real-time data, because it is generally easier and more affordably implemented than other ingestion options.
AWS Solutions:
AWS Glue(ETL tool), AWS Database Migration, AWS Step Functions.
(You can automate various ETL tasks that involve complex workflows by using AWS Step Functions.)
Stream Processing
Stream processing manipulates and loads data as it’s recognized in real time.
AWS Solutions:
**Amazon Kinesis **
Identify and implement a data transformation solution
Some Solutions:
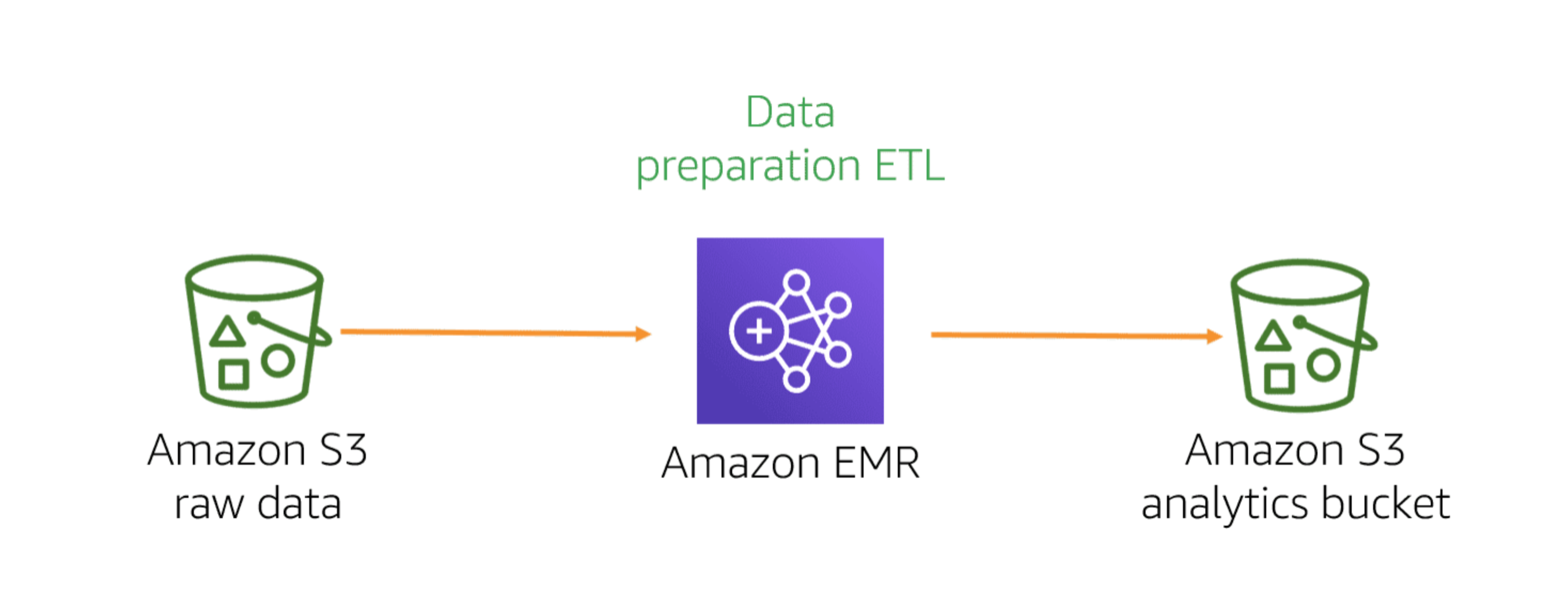
- Using Apache Spark on Amazon EMR provides a managed framework
-
If your datasets or computations are not optimally compatible with SQL, you can use AWS Glue to seamlessly run Spark jobs (Scala and Python support) on data stored in your Amazon S3 buckets.
-
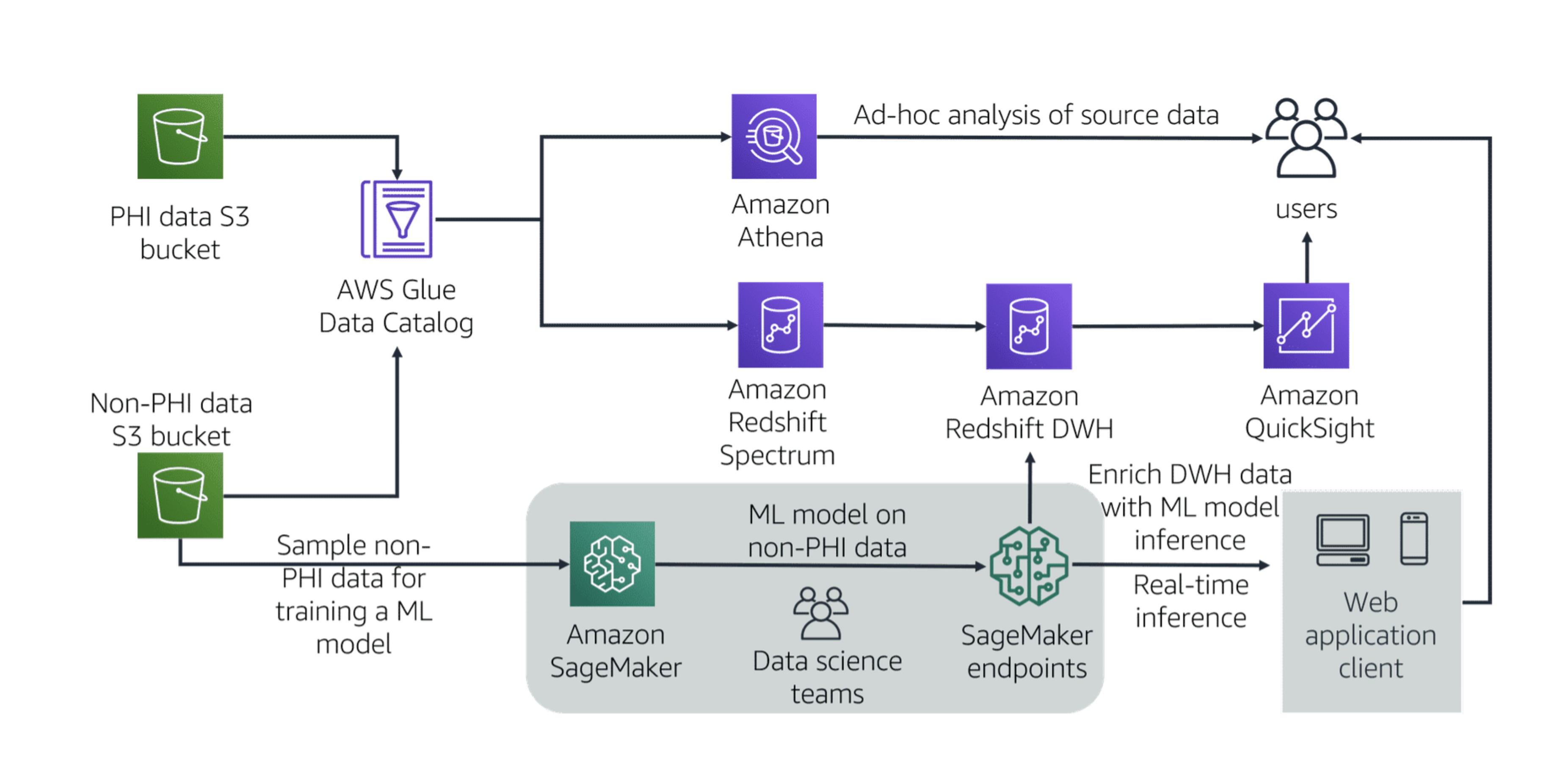
You can store a single source of data in Amazon S3 and perform ad hoc analysis.
This reference architecture shows how AWS services for big data and ML can help build a scalable analytical layer for healthcare data. Customers can store a single source of data in Amazon S3 and perform ad hoc analysis with Athena, integrate with a data warehouse on Amazon Redshift, build a visual dashboard for metrics using Amazon QuickSight, and build an ML model to predict readmissions using Amazon SageMaker. By not moving the data around and connecting to it using different services, customers avoid building redundant copies of the same data.
Sample Questions
-
A data engineer needs to create a cost-effective data pipeline solution that ingests unstructured data from various sources and stores it for downstream analytics applications and ML. The solution should include a data store where the processed data is highly available for at least one year, so that data analysts and data scientists can run analytics and ML workloads on the most recent data. For compliance reasons, the solution should include both processed and raw data. The raw data does not need to be accessed regularly, but when needed, should be accessible within 24 hours.
ANS:

-
An ad-tech company has hired a data engineer to create and maintain a machine learning pipeline for its clickstream data. The data will be gathered from various sources, including on premises, and will need to be streamed to the company’s Amazon EMR instances for further processing.
ANS:

-
A transportation company currently uses Amazon EMR with Apache Spark for some of its data transformation workloads. It transforms columns of geographical data (like latitudes and longitudes) and adds columns to segment the data into different clusters per city to attain additional features for the k-nearest neighbors algorithm being used.
The company wants less operational overhead for their transformation pipeline. They want a new solution that does not make significant changes to the current pipeline and only requires minimal management.
What AWS services should the company use to build this new pipeline?
- Use AWS Glue to transform files. Use Amazon S3 as the destination. ✅
- Use AWS Glue to transform files. Use Amazon EMR HDFS as the destination. ❌
- Use Amazon EMR to transform files. Use Amazon S3 as the destination. ❌
- Use Lambda to transform files. Use Amazon EMR HDFS as the destination. ❌
Domain 2: EDA
Sample Questions:
-
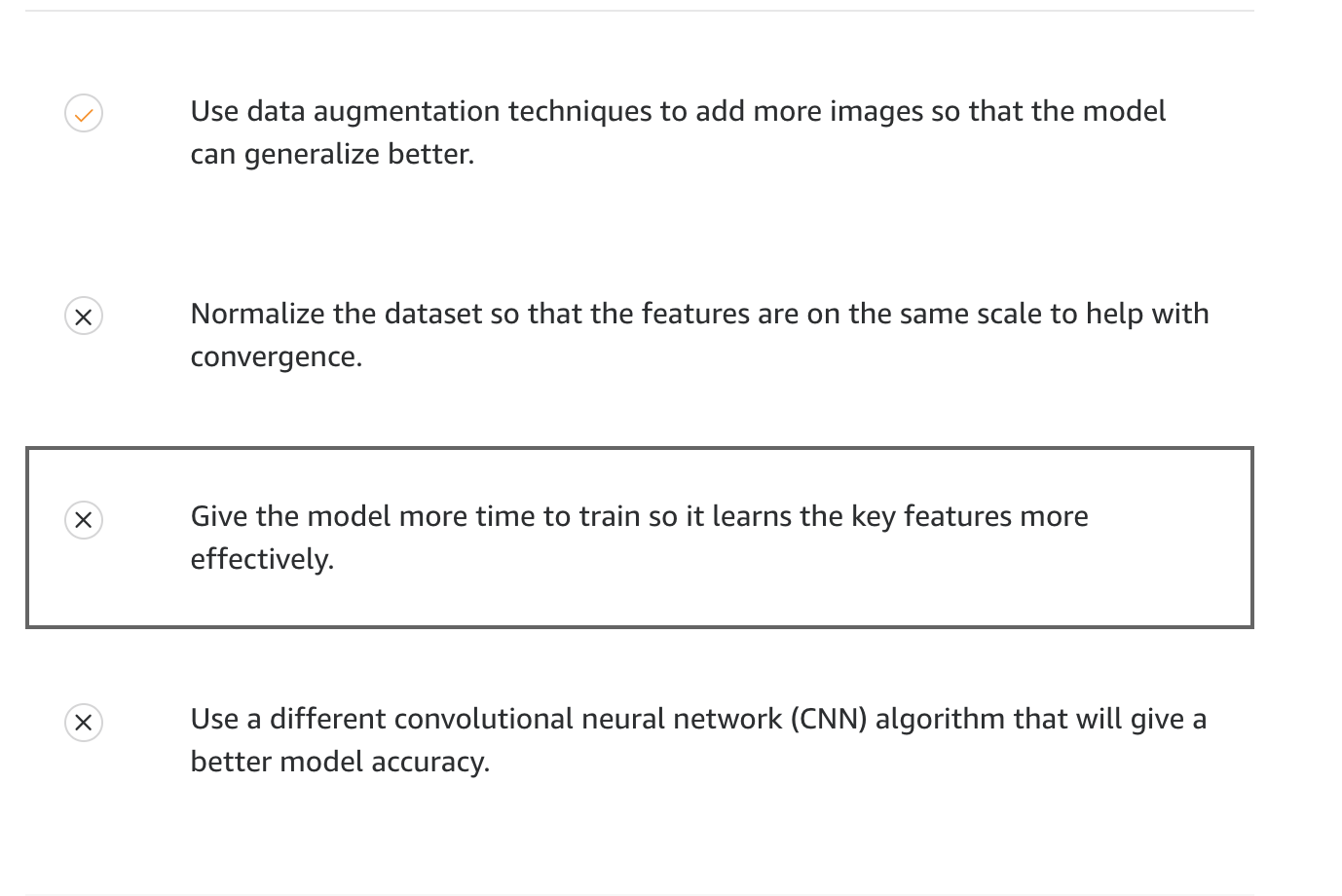
A team of data scientists in a company focusing on security and smart home devices created an ML model that can classify guest types at a front door using a video doorbell. The team is getting an accuracy of 96.23% on the validation dataset.
However, when the team tested this model in production, images were classified with a much lower accuracy. That was due to weather: The changing seasons had an impact on the quality of production images.
What can the team do to improve their model?
-
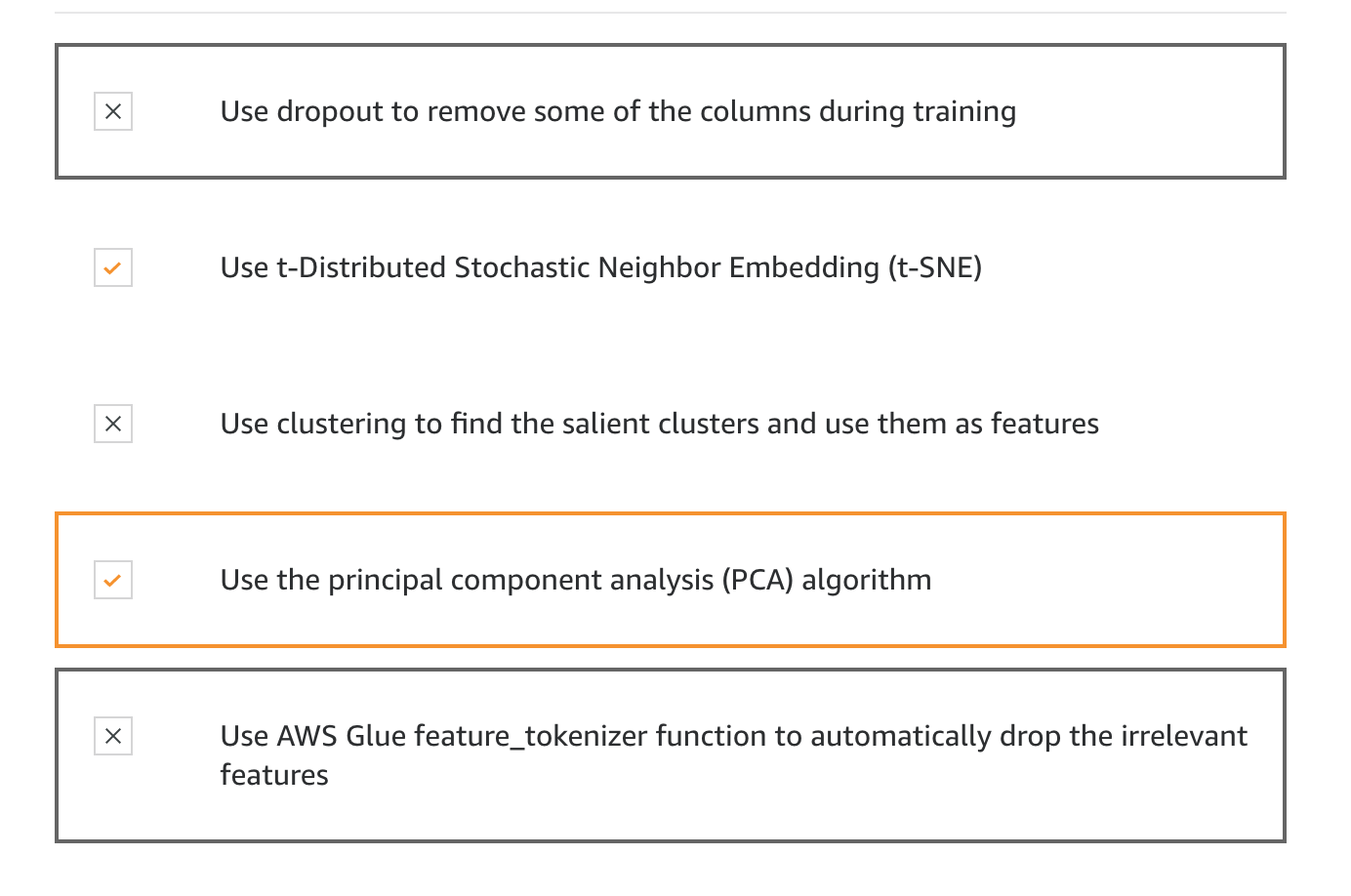
A team of data scientists in a financial company wants to predict the risk for their incoming customer loan applications. The team has decided to do this by applying the XGBoost algorithm, which will predict the probability that a customer will default on a loan. In order to create this solution, the team wants to first merge the customer application data with demographic and location data before feeding it into the model.
However, the dimension of this data is really large, and the team wants to keep only those features that are the most relevant to the prediction.
What techniques can the team use to reach the goal? (Select TWO.)
- AWS glue doesn’t have that shit.
- clustering doesn’t help with dimensionality reduction.
- A helps the dimensionality problem, but doesn’t help the feature selection problem.
-
A social networking organization wants to analyze all the comments and likes from its users to flag offensive language on the site. The organization’s data science team wants to use a Long Short-term Memory (LSTM) architecture to classify the raw sentences from the comments into one of two categories: offensive and non-offensive.
What should the team do to prepare the data for the LSTM?
- Vectorize the sentences. Transform them into numerical sequences. Use the sentences as the input. ❌
- Convert the individual sentences into numerical sequences starting from the number 1 for each word in a sentence. Use the sentences as the input. ❌
- Convert the individual sentences into sequences of words. Use those as the input. ❌
- Vectorize the sentences. Transform them into numerical sequences with a padding. Use the sentences as the input. ✅
Domain 3: Modeling
3.1 Frame Business Problems as ML problems
Regression problem(prediction) vs classification problem
3.2 Select the appropriate model(s) for an ML problem
Amazon SageMaker provides a few built-in algorithms that work for classification situations: Linear Learner, XGBoost, and K-Nearest Neighbors. XGBoost, for instance, is an open-source implementation of the gradient-boosted trees algorithm. Gradient boosting is a supervised learning algorithm that attempts to accurately predict a target variable by combining an ensemble of estimates from a set of simpler, weaker models.
In terms of the built-in Amazon SageMaker algorithms you could choose for regression problems, it’s pretty similar. Again, you could choose Linear Learner and XGBoost. The difference is that you set the hyperparameters to direct these algorithms to produce quantitative results.
There are Amazon SageMaker built-in algorithms for natural language processing:
- BlazingText algorithm provides highly optimized implementations of the Word2vec and text classification algorithms.
- Sequence2sequence is a supervised learning algorithm where the input is a sequence of tokens (for example, text, audio) and the output generated is another sequence of tokens.
- Object2Vec generalizes the well-known Word2Vec embedding technique for words that are optimized in the Amazon SageMaker BlazingText algorithm.
There are Amazon SageMaker built-in algorithms for computer vision:
- Image classification is a supervised learning algorithm used to classify images.
- Object detection algorithm detects and classifies objects in images using a single deep neural network. It is a supervised learning algorithm that takes images as input and identifies all instances of objects within the image scene. The object is categorized into one of the classes in a specified collection with a confidence score that it belongs to the class. Its location and scale in the image are indicated by a rectangular bounding box.
- Semantic segmentation algorithm tags every pixel in an image with a class label from a predefined set of classes.
Other options for training algorithms
- Use Apache Spark with Amazon SageMaker
- Submit custom code to train a model with a deep learning framework like TensorFlow or Apache MXNet
- Use your own custom algorithm and put the code together as a Docker image
- Subscribe to an algorithm from AWS Marketplace
3.3: Train ML models
Cross Validation
Sage Maker
3.4: Perform hyperparameter optimization
What are hyperparameters?
Hyperparameters are the knobs or settings that can be tuned before running a training job to control the behavior of an ML algorithm. They can have a big impact on model training as it relates to training time, model convergence, and model accuracy. Unlike model parameters that are derived from the training job, the values of hyperparameters do not change during the training.
There are different categories of hyperparameters
Model hyperparameters
Model hyperparameters define the model itself—Attributes of a neural network architecture like filter size, pooling, stride, padding
Optimizer hyperparameters
Optimizer hyperparameters, are related to how the model learn the patterns based on data and are used for a neural network model. These types of hyperparameters include optimizers like gradient descent and stochastic gradient descent, or even optimizers using momentum like Adam or initializing the parameter weights using methods like Xavier initialization or He initialization
Data hyperparameters
Data hyperparameters are related to the attributes of the data, often used when you don’t have enough data or enough variation in data—Data augmentation techniques like cropping, resizing
Tuning hyperparameters can be very labor-intensive
Traditionally, this was done manually: someone who has domain experience related to that hyperparameter and the use case would manually select the hyperparameters based on their intuition and experience. Then they would train the model and score it on the validation data. This process would be repeated over and over again until satisfactory results are achieved.
A better way is to use search methods to tune hyperparameters:
Grid search and Random search
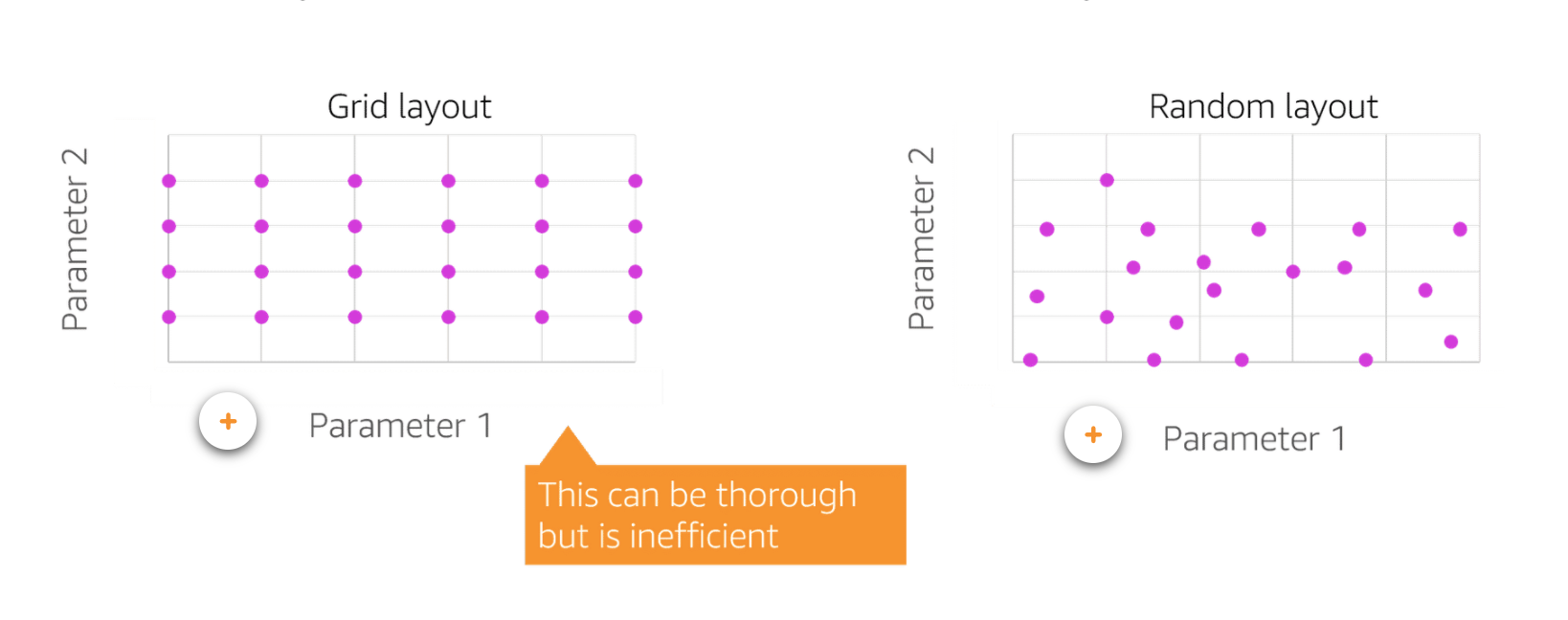
- Grid Search: you can set up a grid made of hyperparams and their different values. For each possible combination, a model is trained and a score is produced on the validation data. With this approach, every single combination of the given possible hyperparams values is tried. Therefore this method could be very inefficient.
- Random Search: similar to grid search, but random combinations are selected. You can set the number of search iterations based on time and resource constrains.
AWS Solution: SageMaker
Then there’s automated hyperparameter tuning, which uses methods like gradient descent, Bayesian optimization, and evolutionary algorithms to conduct a guided search for the best hyperparameter settings.
3.5: Evaluate ML models
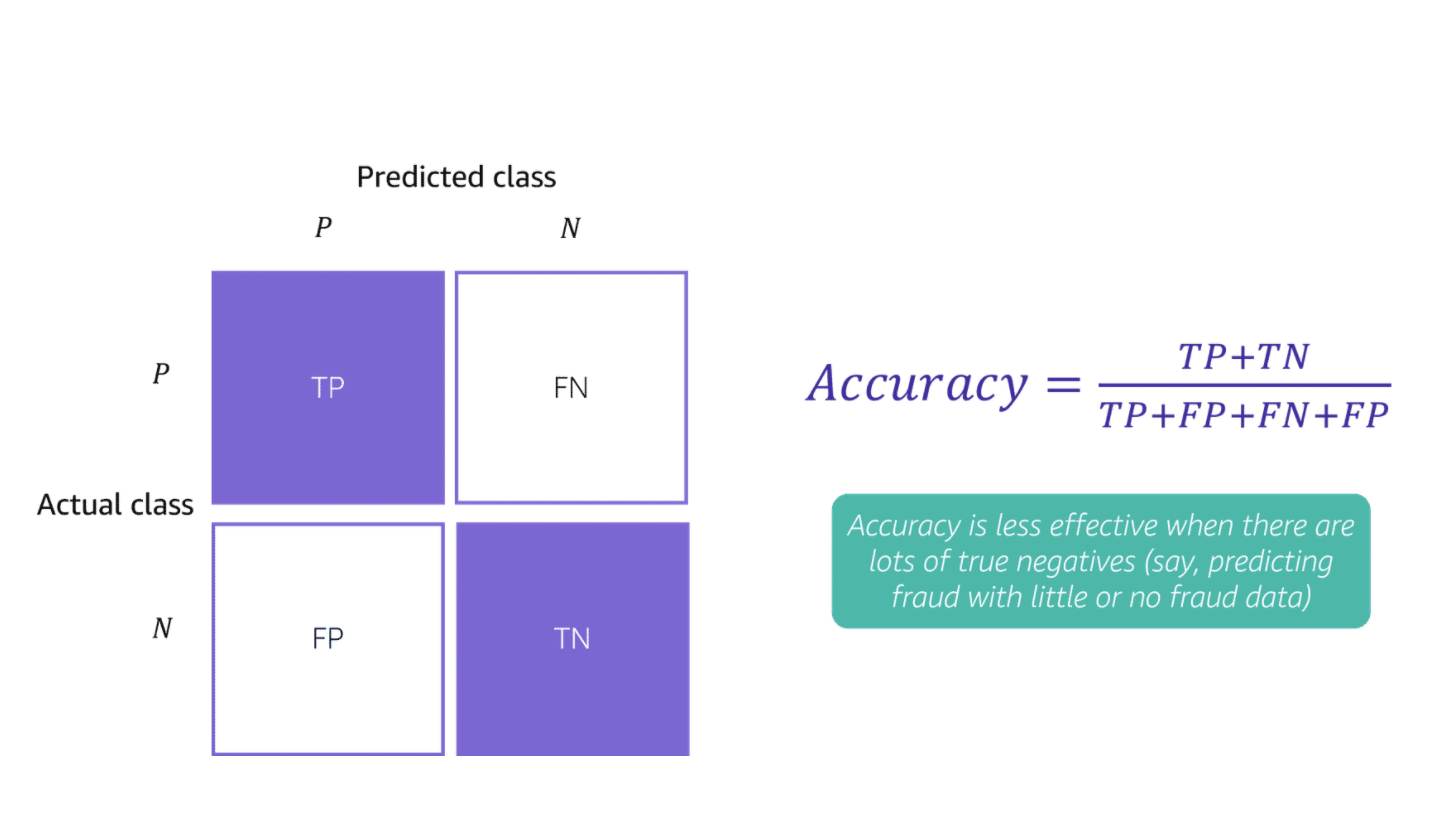
Confusion Matrix
**Metrics for classification problems **
Accuracy is the ratio of correct predictions to total number of predictions
Precision is the proportion of positive predictions that are actually correct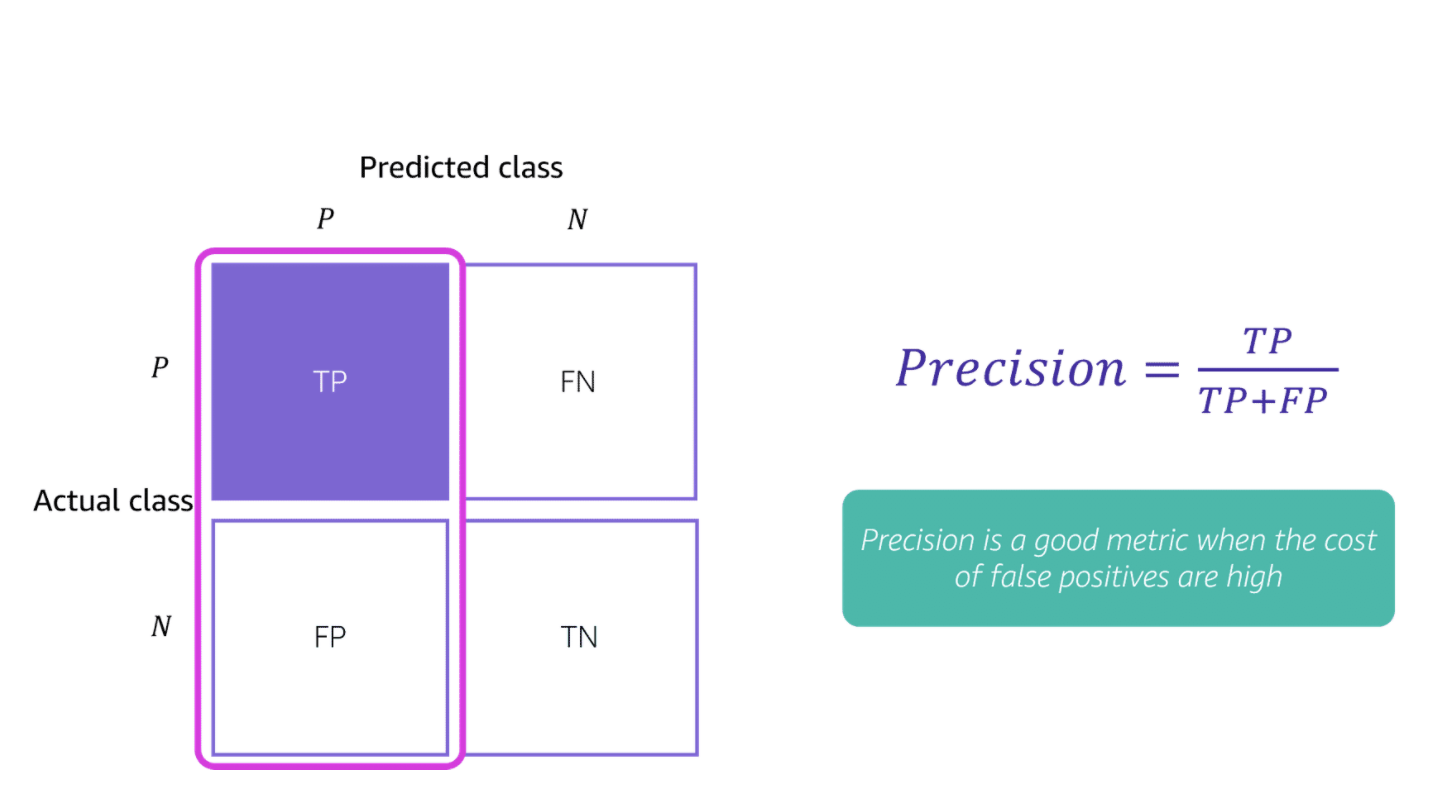
Recall is the proportion of correct sets that are identified as positive
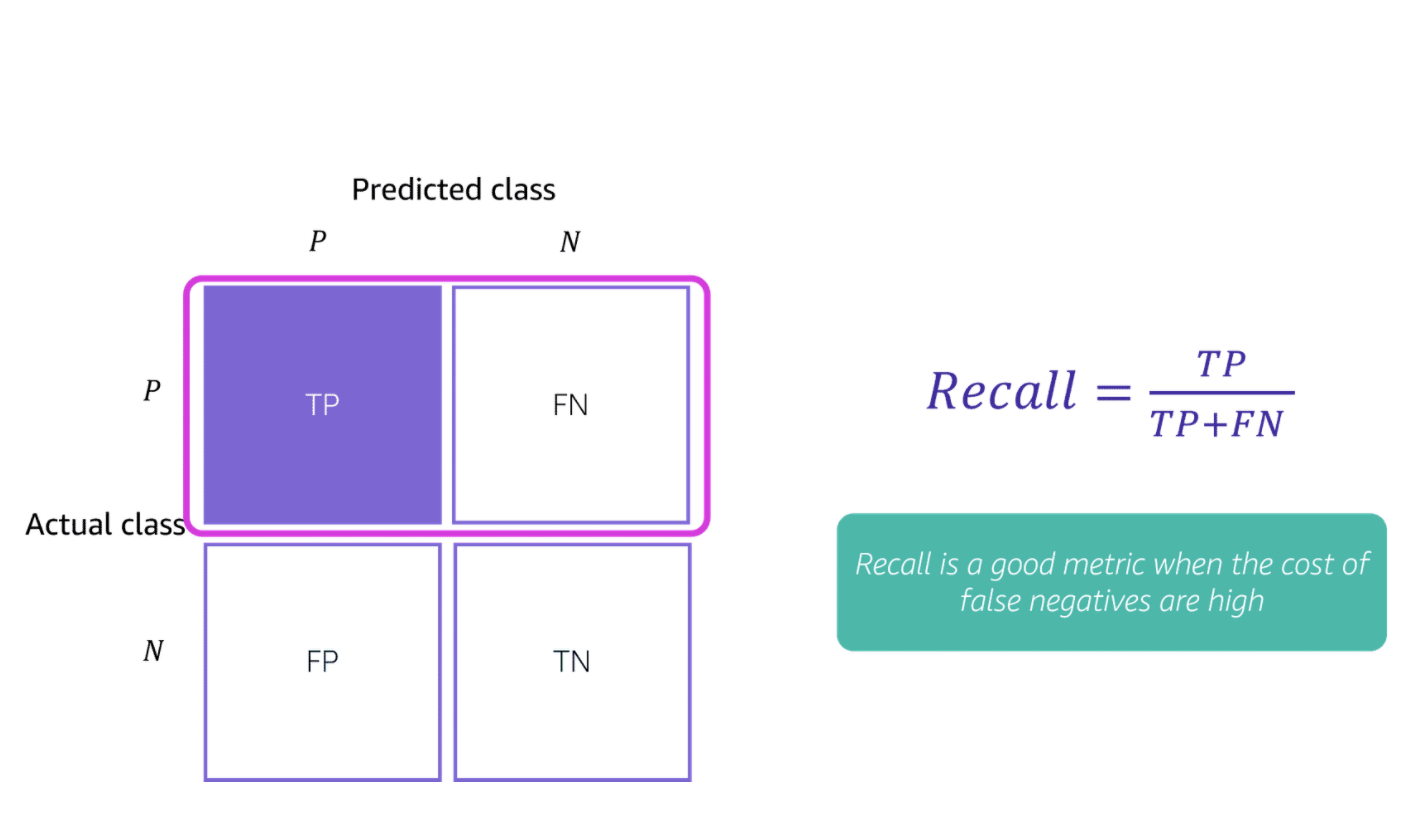
Additional metrics include:
- F1 score:
$$ (2PrecisionRecall)/(Precision+Recall) $$
- AUC(Area under the Curve) - Receiver Operator Curve(ROC)
Sample Questions
-
An oil and natural gas company is using machine learning to discover prime locations for drilling. The company has chosen Amazon SageMaker as its service for creating machine learning models. The company’s data scientists are using notebook instances to develop those models. However, the data scientists spend a long time waiting for the training jobs to complete.
The company wants improve this idle time to more effectively iterate on the models with minimal change to the code to enable data scientists to quickly experiment with their models without having to wait for the training job to load the data and train the model.
What should the team of data scientists do to solve this issue?
- Use Amazon SageMaker in-built algorithms. ❌
- Use Amazon SageMaker Estimators in local mode to train the models. ✅
- Change the training job to use Pipe Mode to improve the time it takes to train the model. ❌
- Create the models on local laptops. Then, port the code over to use Amazon SageMaker. ❌
Notes:
A & C are for training algos, they can’t help DS to quickly experiment the models.
B is to avoid the loading time for data.
-
A data scientist trained an XGBoost model to classify internal documents for further inquiry, and now wants to evaluate the model’s performance by looking at the results visually.
What technique should the data scientist use in this situation?
- Scatterplot to visualize the predicted labels versus the true label. ❌
- Correlation matrix to visualize the predicted labels versus the true label. ❌
- Confusion matrix to visualize the predicted labels ✅
- Box plot to visualize the predicted labels (X axis) versus the true labels (Y axis). ❌
-
A manufacturing company wants to increase the longevity of its factory machines by predicting when a machine part is about to stop working, jeopardizing the health of the machine. The company’s team of Data Scientists will build an ML model to accomplish this goal. The model will be trained on data made up of consumption metrics from similar factory machines, and will span a time frame from one hour before a machine part broke down to five minutes after the part degraded.
What kind of machine learning algorithm should the company use to build this model?
- Convolutional neural network (CNN) ❌
- Amazon SageMaker DeepAR ✅
- Scikit Learn Random Forest ❌
- SciKit Learn Regression ❌
-
A Data Scientist working for an autonomous vehicle company is building an ML model to detect and label people and various objects (for instance, cars and traffic signs) that may be encountered on a street. The Data Scientist has a dataset made up of labeled images, which will be used to train their machine learning model.
What kind of ML algorithm should be used?
- Instance segmentation ✅
- Image localization ❌
- Image classification ❌
- Semantic segmentation ❌
-
A Data Scientist is training a convolutional neural network model to detect incoming employees at the company’s front gate using a camera so that the system opens for them automatically. However, the model is taking too long to converge and the error oscillates for more than 10 epochs.
What should the Data Scientist do to improve upon this situation? (Select TWO.)
- Increase batch size ❌
- Add more epochs ❌
- Decrease weight decay ❌
- Normalize the images before training ✅
- Add batch normalization ✅
Domain 4: ML Implementation and Operations
4.1: Build ML solutions for performance, availability, scalability, resiliency, and fault tolerance
High availability and fault tolerance
At the heart of designing for failure are two concepts known as high availability and fault tolerance.
In a highly available solution, the system will continue to function even when any component of the architecture stops working. A key aspect of high availability is fault tolerance, which, when built into an architecture, ensures that applications will continue to function without degradation in performance, despite the complete failure of any component of the architecture.
One method of achieving high availability and fault tolerance is loose coupling
With a loosely coupled, distributed system, the failure of one component can be managed in between your application tiers so that the faults do not spread beyond that single point. Loose coupling is often achieved by making sure application components are independent of each other. For example, you should always decouple your storage layer with your compute layer because a training job only requires minimal time, but storing data is permanent. Decoupling helps turn off the compute resources when they are not needed.
Loosely & tightly coupled system:
Tightly coupled:
- More interdependency
- More coordination
- More information
⬇️
Loosely coupled:
- Less interdependency
- Less coordination
- Less information
Queues are used in loose coupling to pass messages between components
AWS SQS (queue service), AWS Step Function(workflow service)

Amazon CloudWatch helps you monitor your system
AWS CloudTrail captures API calls and related events
AWS CloudTrail captures API calls and related events made by or on behalf of your AWS account and delivers the log files to an Amazon S3 bucket that you specify. You can identify which users and accounts called AWS, the source IP address from which the calls were made, and when the calls occurred.
**You can design for failure of any individual component by leveraging key AWS services and features **
AWS GLUE and EMR
You should decouple your ETL process from the ML pipeline. The compute power needed for ML isn’t the same as what you’d need for an ETL process—they have very different requirements.
- An ETL process needs to read in files from multiple formats, transform them as needed, and then write them back to a persistent storage. Keep in mind that reading and writing takes a lot of memory and disk I/O, so when you decouple your ETL process, use a framework like Apache Spark, which can handle large amounts of data easily for ETL.
- Training, on the other hand, may require GPUs which are much more suited to handle the training requirements than CPUs. However, GPUs are less cost-effective to keep running when a model is not being trained. So you can make use of this decoupled architecture by simply using an ETL service like AWS Glue or Amazon EMR, which use Apache Spark for your ETL jobs and Amazon SageMaker to train, test, and deploy your models.
AMS SageMaker Endpoints
To ensure a highly available ML serving endpoint, deploy Amazon SageMaker endpoints backed by multiple instances across Availability Zones.
AMS SageMaker
Amazon SageMaker makes it easy to containerize ML models for both training and inference. In doing so, you can create ML models made up of loosely coupled, distributed services that can be placed on any number of platforms, or close to the data that the applications are analyzing.
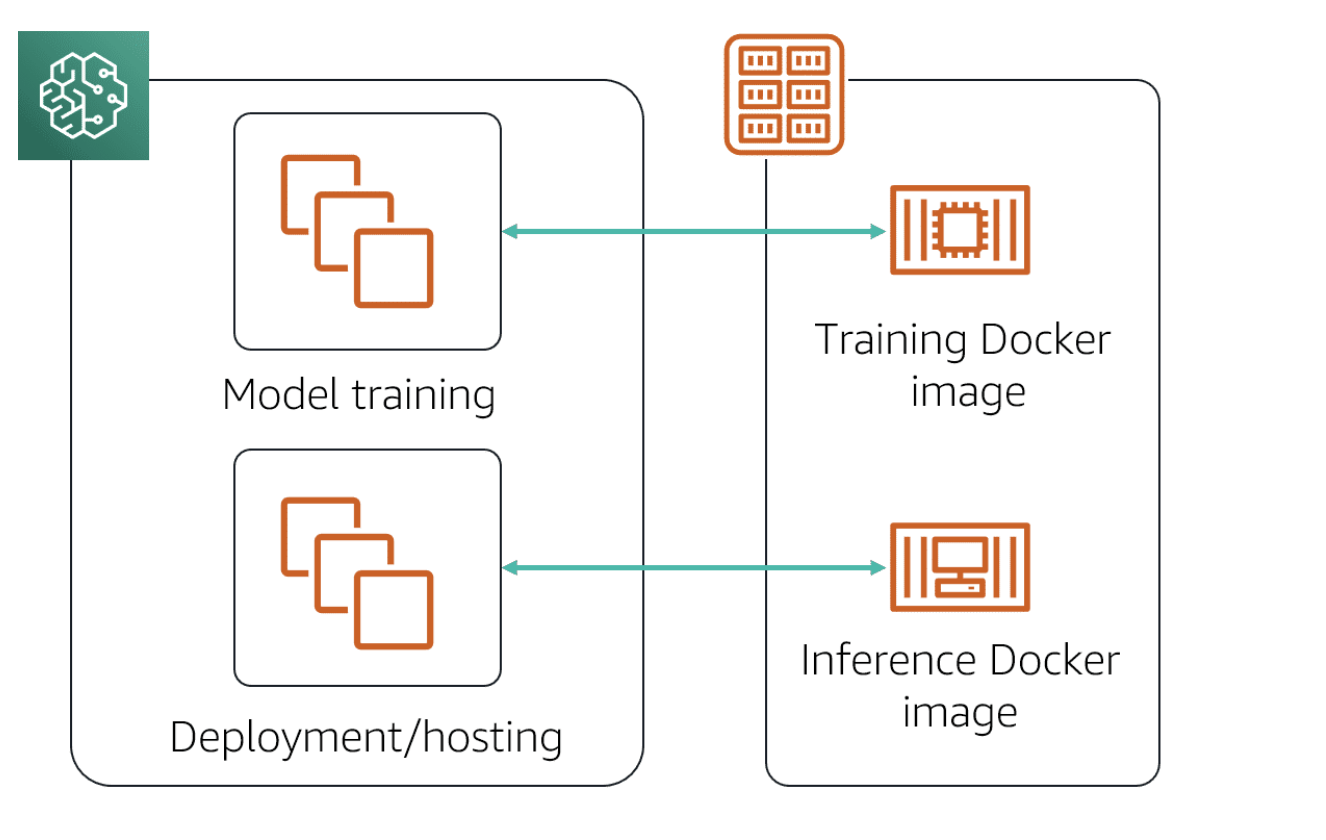
AWS Auto Scaling
Use AWS Auto Scaling to build scalable solutions by configuring automatic scaling for the AWS resources such as Amazon SageMaker endpoints that are part of your application in response to the changes in traffic to your application.
With AWS Auto Scaling, you configure and manage scaling for your resources through a scaling plan. The scaling plan uses dynamic scaling and predictive scaling to automatically scale your application’s resources.
This ensures that you add the required computing power to handle the load on your application, and then remove it when it’s no longer required. The scaling plan lets you choose scaling strategies to define how to optimize your resource utilization. You can optimize for availability, for cost, or a balance of both.
As you increase the number of concurrent prediction requests, at some point the endpoint responds more slowly and eventually errors out for some requests. Automatically scaling the endpoint avoids these problems and improves prediction throughput. When the endpoint scales out, Amazon SageMaker automatically spreads instances across multiple Availability Zones. This provides Availability Zone-level fault tolerance and protects from an individual instance failure.
If the endpoint has only a moderate load, you can run it on a single instance and still get good performance. Use automatic scaling to ensure high availability during traffic fluctuations without having to constantly provision for peak traffic. For production workloads, use at least two instances. Because Amazon SageMaker automatically spreads the endpoint instances across multiple Availability Zones, a minimum of two instances ensures high availability and provides individual fault tolerance.
To determine the scaling policy for automatic scaling in Amazon SageMaker, test for how much load (RPS) the endpoint can sustain. Then configure automatic scaling and observe how the model behaves when it scales out. Expected behavior is lower latency and fewer or no errors with automatic scaling.
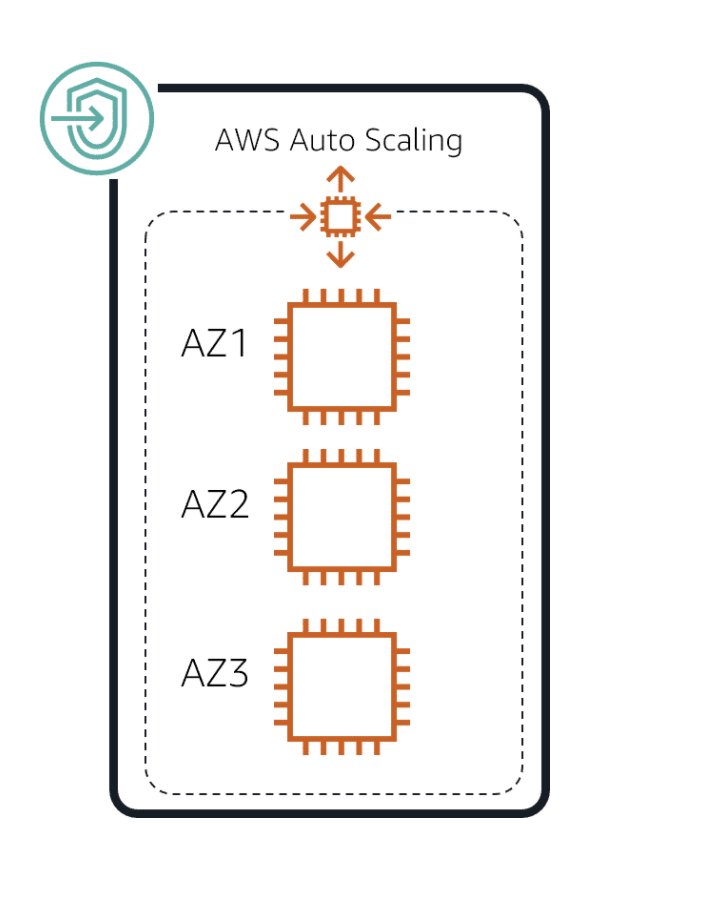
Remark:
Auto Scaling Group
What is ASG?
In real life, the load on your websites and app can change; in the cloud, you can create and get rid of servers very quickly.
ASG is used to:
- Scale out(which is add EC2 instances) to match an increased load.
- Scale in (which is remove EC2 instances) to match a decreased load.
- Ensure we have a min and max number of machines running
- Automatically register new instances to a load balancer
4.2: Recommend and implement the appropriate ML services and features for a given problem
The stack for Amazon machine learning has three tiers
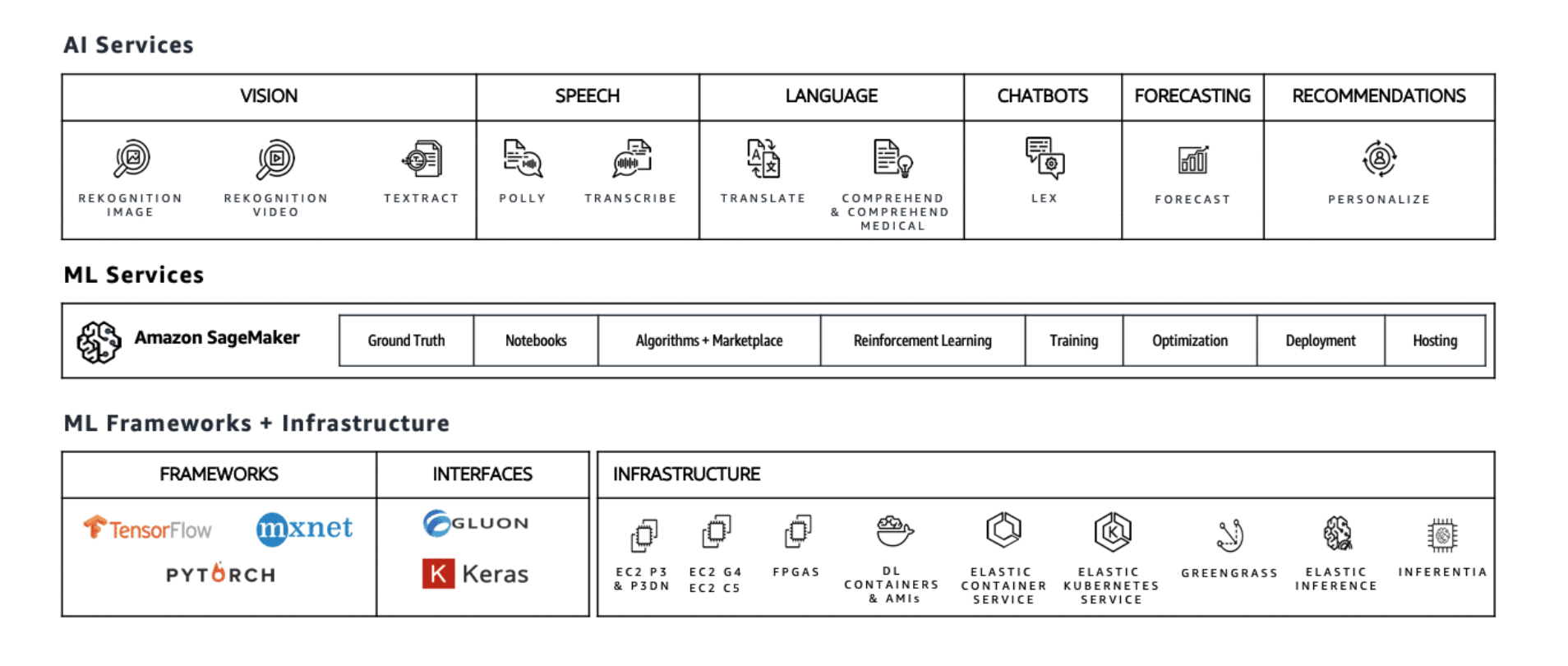
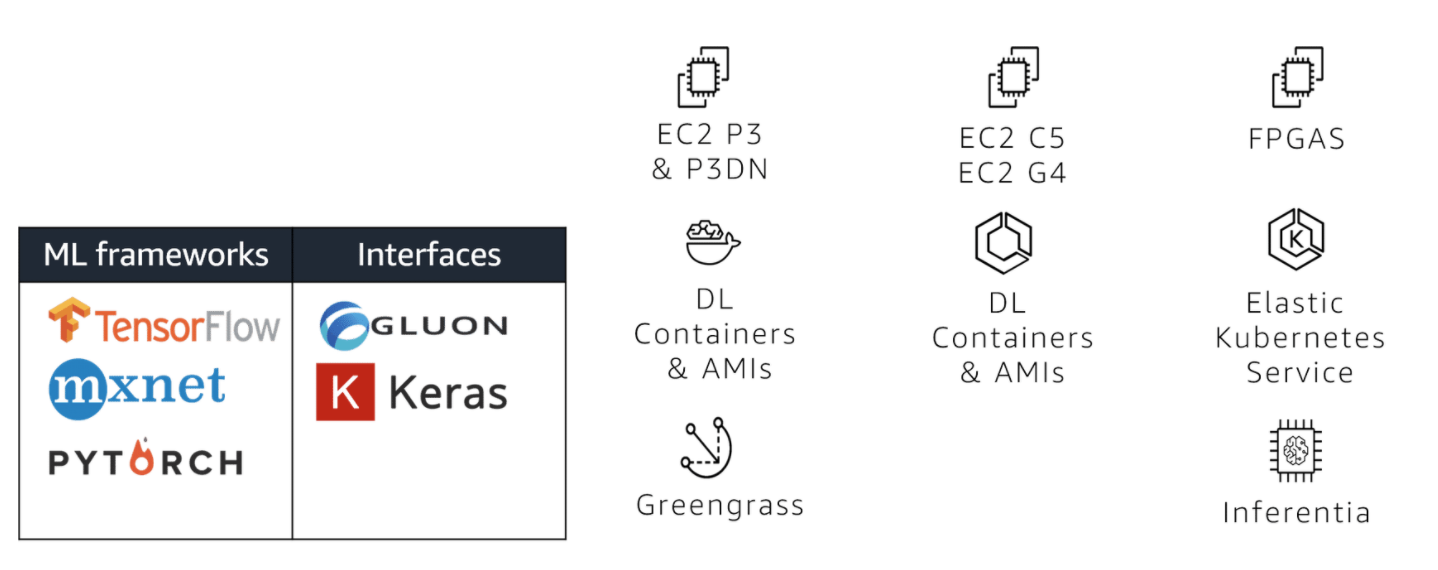
ML frameworks + infrastructure
The bottom tier of the stack is for expert ML practitioners who work at the framework level. To work with these frameworks, you are comfortable building, training, tuning, and deploying ML models on the metal, so to speak. ML frameworks are the foundation from which innovation in ML is designed. The focus here is on making it easier for you to connect more broadly to the AWS ecosystem, whether that’s about pulling in IoT data from AWS IOT Greengrass, accessing state-of-the art chips (P3), or leveraging elastic inference.
The vast majority of deep learning and ML in the cloud is done on P3 instances in AWS. You can use whichever ML deep learning framework you like, but some popular options are TensorFlow, MXNet, and PyTorch, which are all supported on AWS.
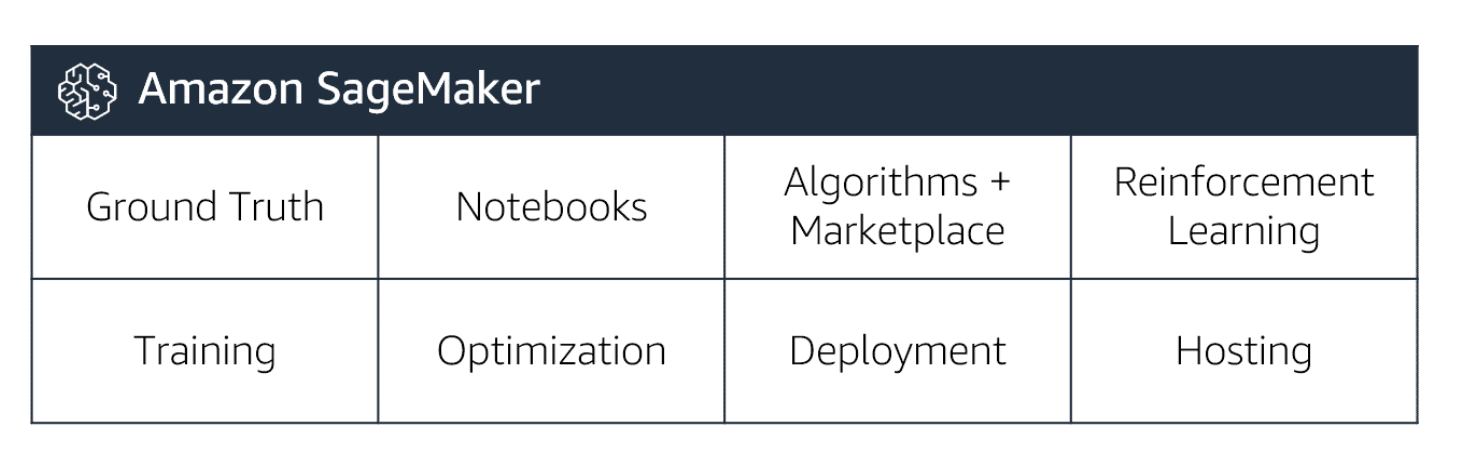
ML Services
AWS SageMaker is the heart of this tier.
AI Services
AWS services in the top tier are for customers who really don’t want to deal with building and training their ML models. All of that has been abstracted away, leaving you with easy-to-use services designed to help you deal with common ML problems in various domains, like computer vision, NLP, and time series forecasting.
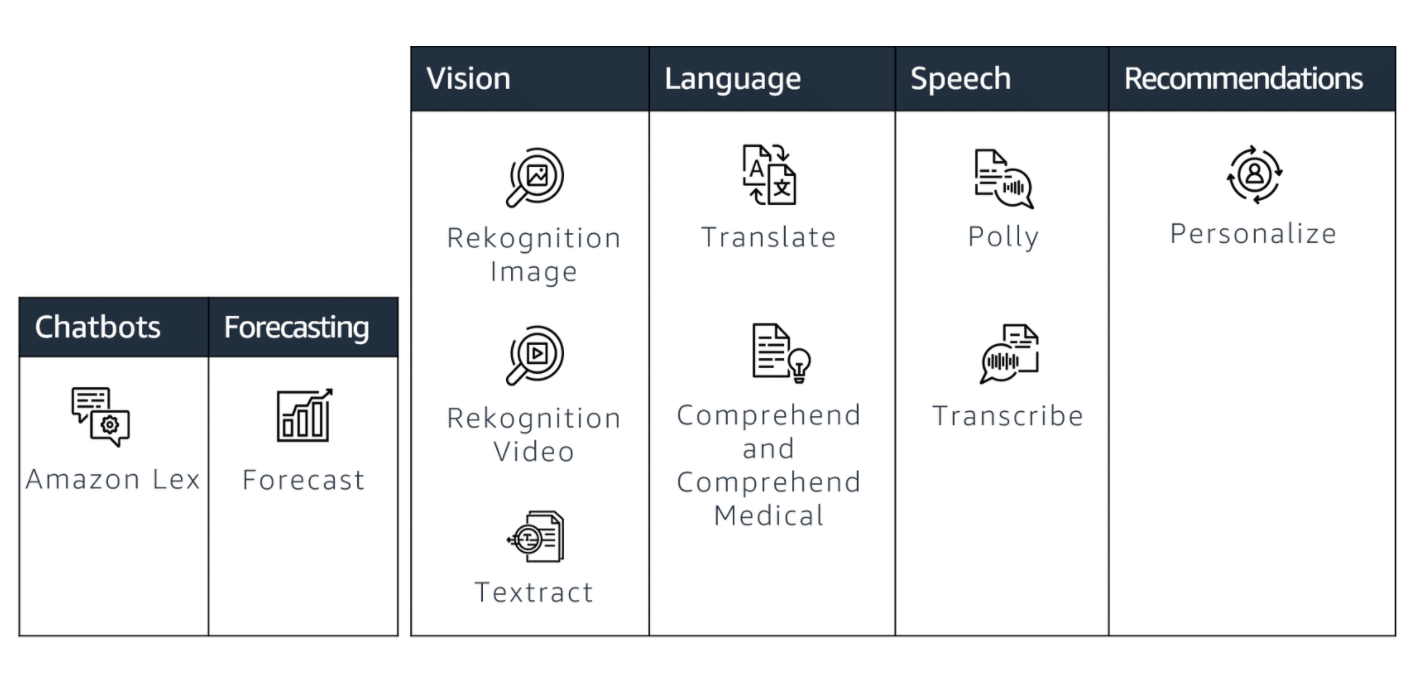
Amazon AI services
- Amazon Translate
- Amazon Lex
- Amazon Polly
- Amazon Transcribe
- Amazon Rekognition
- Amazon Comprehend
4.3: Apply Basic AWS security practices to ML solutions
Below is a summary of security features integrated with Amazon SageMaker
- Authentication
- IAM federation
- Gaining insight
- Restrict access by IAM policy and condition keys
- Audit
- API logs to AWS CloudTrail - exception of InvokeEndpoint
- Data Protection at rest
- AWS KMS-based encryption for:
- Notebooks
- Training jobs
- Amazon S3 location to store modelsEndpoint
- AWS KMS-based encryption for:
- Data Protection at motion
- HTTPS for:
- API/console
- Notebooks
- VPC-enabled
- Interface endpoint
- Limit by IPTraining jobs/endpoints
- HTTPS for:
4.4: Deploy and operationalize ML solutions
Deploying a model using Amazon SageMaker hosting services is a three-step process
Create a model in Amazon SageMaker
You need:
- The Amazon S3 path where the model artifacts are stored
- The Docker registry path for the image that contains the inference code
- A name that you can use for subsequent deployment steps
Create an endpoint configuration for an HTTPS endpoint
You need:
- The name of one or more models in production variants
- The ML compute instances that you want Amazon SageMaker to launch to host each production variant. When hosting models in production, you can configure the endpoint to elastically scale the deployed ML compute instances. For each production variant, you specify the number of ML compute instances that you want to deploy. When you specify two or more instances, Amazon SageMaker launches them in multiple Availability Zones. This ensures continuous availability. Amazon SageMaker manages deploying the instances.
Create an HTTPS endpoint
You need to provide the endpoint configuration to Amazon SageMaker. The service launches the ML compute instances and deploys the model or models as specified in the configuration.
You may want to pay extra attention to the following points when you’re delivering an ML model into a production environment:
- Apply software engineering disciplines. Add error recovery code and make sure that tests for unexpected data inputs exist. Perform the same kind of unit testing, quality assurance, and user acceptance testing that is performed for other systems. If the ML system has moved from the research stage to development, some of these expected software engineering practices might have been inconsistently applied. Automate this system using common DevOps tools like AWS CodeBuild and AWS CodeCommit.
- Track, identify, and account for changes in data sources. The data might change over time. One change in data type in one source can break the whole pipeline. Changes in software that produces a data source can have flow-on effects.
- Perform ongoing monitoring and evaluation of results. Evaluate the expectations versus the results of the ML system. Build methods to check the error rate and the classes of errors being made against project expectations. If the overall error rate is the same, are the same proportions of the different classes of errors still the same? Is model drift occurring?
- Create methods to collect data from production inferences that can be used to improve future models.
Amazon SageMaker supports automatic scaling for production variants
Amazon SageMaker supports automatic scaling for production variants. Automatic scaling dynamically adjusts the number of instances provisioned for a production variant in response to changes in your workload. When the workload increases, automatic scaling brings more instances online. When the workload decreases, automatic scaling removes unnecessary instances so that you don’t pay for provisioned variant instances that you aren’t using.

Define and apply a scaling policy that uses Amazon CloudWatch metrics
- Automatic scaling uses the policy to adjust the number of instances up or down in response to actual workloads
- You can use the AWS Management Console to apply a scaling policy based on a predefined metric
- A predefined metric is defined in an enumeration so you can specify it by name in code or use it in the console
- Always load-test your automatic scaling configuration to ensure that it works correctly before using it to manage production traffic
Sample Questions:
-
A sports and betting company uses machine learning to predict the odds of winning during sporting events. It uses the Amazon SageMaker endpoint to serve its production model. The endpoint is on an m5.8xlarge instance.
What can the company do to ensure that this endpoint is highly available, while using the most cost-effective and easily managed solution?
- Create another endpoint. Put the two endpoints behind an Application Load Balancer. ❌
- Increase the number of instances associated with the endpoint to more than one. ✅
- Increase the instance size to m5.16 x-large. ❌
- Add an elastic inference to the endpoint. ❌
-
A healthcare company wants to deploy an ensemble of models behind a single endpoint with minimal management. The models include an XGBoost model trained on one of its structured datasets and a CNN model trained on an image dataset.
Which solution can the company use to reach this objective?
-
Create an AWS Lambda function with Amazon API Gateway that preprocesses the incoming data. The function then creates the prediction from all the ensemble models. And finally, it returns the prediction. ✅
-
Create an AWS Deep Learning container that preprocesses the incoming data. The container then creates the prediction from all the ensemble models. And finally, it returns the prediction. ❌
-
Create an Amazon EC2 instance with the AWS Deep Learning AMI that preprocesses the incoming data. The instance then creates the prediction from all the ensemble models. And finally, it returns the prediction. ❌
-
Create an Amazon SageMaker endpoint that preprocesses the incoming data. The endpoint then creates the prediction from all the ensemble models. And finally, it returns the prediction. ❌
-
-
A Machine Learning Engineer created a pipeline for training an ML model using an Amazon SageMaker training job. The training job began successfully, but then failed after running for five minutes.
How should the Engineer begin to debug this issue? (Select TWO.)
- Check AWS CloudTrail logs to check the error that caused the training to fail
- Log into the Amazon SageMaker training job instance and check the job history
- Go to Amazon CloudWatch logs and check the logs for the given training job ✅
- Check the error in the given training job directly in the Amazon SageMaker console
- Call the DescribeJob API to check the FailureReason option✅
-
A news organization wants to extract metadata from its articles and blogs and index that metadata in Amazon Elasticsearch Service (Amazon ES) to enable faster searches.
What AWS service can the organization use to achieve this goal?
- Amazon Textract
- Amazon Personalize
- Amazon Rekognition Image
- Amazon Comprehend ✅
-
A news organization wants to extract metadata from its articles and blogs and index that metadata in Amazon Elasticsearch Service (Amazon ES) to enable faster searches.
What AWS service can the organization use to achieve this goal?
- Amazon Textract
- Amazon Personalize
- Amazon Rekognition Image
- Amazon Comprehend ✅
-
A machine translation company is deploying its language translation models behind an Amazon SageMaker endpoint. The company wants to deploy a solution directly on its website so that users can input text in one language and have it translated into a second language. The company wants to reach a solution with minimal maintenance and latency for spiky traffic times.
How should the company architect this solution?
- Create a function on an Amazon EC2 instance that uses CURL to call the InvokeEndpoint API. Call the Amazon EC2 instance from the website.
- Use Lambda to call InvokeEndpoint. Use the Amazon API Gateway URL to call the AWS Lambda function. ✅
- Use Amazon SageMaker InvokeEndpoint with API Gateway
- Install the sagemaker-runtime library on the web server. Call InvokeEndpoint from the webserver.
-
A Machine Learning Specialist has various CSV training datasets stored in an S3 bucket. Previous models trained with similar training data sizes using the Amazon SageMaker Linear learner algorithm have a slow training process. The Specialist wants to decrease the amount of time spent on training the model.
Which combination of steps should be taken by the Specialist? (Select TWO.)
- Convert the CSV training dataset into Apache Parquet format.
- Train the model using Amazon SageMaker Pipe mode. ✅
- Convert the CSV training dataset into Protobuf RecordIO format. ✅
- Train the model using Amazon SageMaker File mode.
- Stream the dataset into Amazon SageMaker using Amazon Kinesis Firehose to train the model.
-
A Machine Learning Specialist is using a 100GB EBS volume as a storage disk for an Amazon SageMaker instance. After running a few training jobs, the Specialist realized that he needed a higher I/O throughput and a shorter job startup and execution time.
Which approach will give the MOST satisfactory result based on the requirements?
- Store the training dataset in Amazon S3 and use the Pipe input mode for training the model. ✅
- Increase the size of the EBS volume to obtain higher I/O throughput.
- Upgrade the SageMaker instance to a larger size.
- Increase the EBS volume to 500GB and use the File mode for training the model.
-
A graphics design startup is using multiple Amazon S3 buckets to store high-resolution media files for their various digital artworks. After securing a partnership deal with a leading media company, the two parties shall be sharing digital resources with one another as part of the contract. The media company frequently performs multiple object retrievals from the S3 buckets every day, which increased the startup’s data transfer costs.
As the Solutions Architect, what should you do to help the startup lower their operational costs?
- Advise the media company to create their own S3 bucket. Then run the
aws s3 sync s3://sourcebucket s3://destinationbucketcommand to copy the objects from their S3 bucket to the other party’s S3 bucket. In this way, future retrievals can be made on the media company’s S3 bucket instead. - Enable the Requester Pays feature in all of the startup’s S3 buckets to make the media company pay the cost of the data transfer from the buckets. ✅
- Create a new billing account for the social media company by using AWS Organizations. Apply SCPs on the organization to ensure that each account has access only to its own resources and each other’s S3 buckets.
- Provide cross-account access for the media company, which has permissions to access contents in the S3 bucket. Cross-account retrieval of S3 objects is charged to the account that made the request.
- Advise the media company to create their own S3 bucket. Then run the
-
A government agency recently decided to modernize its network infrastructure using AWS. They are developing a solution to store confidential files containing Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and other sensitive financial records of its citizens. All data in the storage solution must be encrypted both at rest and in transit. In addition, all of its data must also be replicated in two locations that are at least 450 miles apart from each other.
As a DevOps Engineer, what solution should you implement to meet these requirements?
- Set up primary and secondary S3 buckets in two separate Availability Zones that are at least 450 miles apart. Create a bucket policy to enforce access to the buckets only through HTTPS and enforce S3 SSE-C encryption on all objects uploaded to the bucket. Enable cross-region replication (CRR) between the two buckets.
- Set up primary and secondary S3 buckets in two separate AWS Regions that are at least 450 miles apart. Create a bucket policy to enforce access to the buckets only through HTTPS and enforce S3-Managed Keys (SSE-S3) encryption on all objects uploaded to the bucket. Enable cross-region replication (CRR) between the two buckets. ✅
- Set up primary and secondary Amazon S3 buckets in two separate AWS Regions that are at least 450 miles apart. Create an IAM role to enforce access to the buckets only through HTTPS. Set up a bucket policy to enforce Amazon S3-Managed Keys (SSE-S3) encryption on all objects uploaded to the bucket. Enable cross-region replication (CRR) between the two buckets.
- Set up primary and secondary S3 buckets in two separate Availability Zones that are at least 450 miles apart. Create a bucket policy to enforce access to the buckets only through HTTPS and enforce AWS KMS encryption on all objects uploaded to the bucket. Enable Transfer Acceleration between the two buckets. Set up a KMS Customer Master Key (CMK) in the primary region for encrypting objects.
-
A multinational corporation is using Amazon Athena to analyze the data sets stored in Amazon S3. The Data Analyst needs to implement a solution that will control the maximum amount of data scanned in the S3 bucket and ensure that if the query exceeded the limit, all the succeeding queries will be canceled.
Which of the following approach can be used to fulfill this requirement?
- Set up a workload management (WLM) assignment rule in the primary workgroup.
- Set data limits in the per query data usage control. ✅
- Integrate API Gateway with Amazon Athena. Configure an account-level throttling to control the queries in the S3 bucket.
- Create an IAM policy that will throttle the data limits in the primary workgroup.
-
A company is using Amazon Athena query with Amazon QuickSight to visualize the AWS CloudTrail logs. The Security Administrator created a custom Athena query that reads the CloudTrail logs and checks if there are IAM user accounts or credentials created in the past 29, 30 or 31 days (depending on the current month). However, the Administrator always gets an
Insufficient Permissionserror whenever she tries to run the query from Amazon QuickSight.What is the MOST suitable solution that the Administrator should do to fix this issue?
- Disable the Log File Integrity feature in AWS CloudTrail.
- Enable Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) in the S3 bucket that is used by Athena.
- Use the AWS Account Root User to run the Athena query from Amazon QuickSight.
- Make sure that Amazon QuickSight can access the S3 buckets used by Athena. ✅